Earlier we introduced the personality traits theory of cartel . Now we introduce Eysenck’s personality structure dimensional theory, the Big Five personality, and the Big Six personality.

1. Eysenck’s Dimension Theory of Personality Structure
Eysenck pointed out in his book "Dimensions of Personality": Personality is the sum of the behavioral patterns actually displayed by a living body. He used a method that combined factor analysis and traditional experimental psychology to study personality issues for a long time, and changed his research interest from traits to structural dimensions, thus defining his own personality theory and proposing a four-level model of personality structure.
layer | name | ML15 | factor |
at the upper layer | Type | is composed of traits, which has a large influence range. | General Factor |
The third layer of | The characteristic | is composed of a habit of reaction. ml15 | group factor |
No. 1 The second layer | the habitual reaction layer | consists of recurring daily reactions, often associated with a certain situation | special factors |
the lowest layer | special reaction layer | daily observed reactions, which are more accidental and random | error factor |
example : Extraversion is a type abstracted based on observed internal associations with traits such as sociability, liveliness, activity, and assertiveness. Each trait is abstracted from various habitual reactions (such as partying, lively talkative, arbitrary, etc.), and each habitual reaction is abstracted from the special reactions observed in various special situations. of.
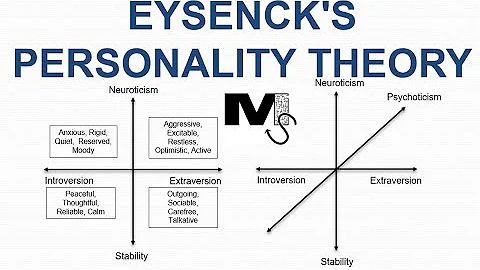
Eysenck proposed three general factors, including: extraversion, neuroticism, and psychoticism, and compiled the Eysenck Personality Questionnaire to measure these three factors.

1. Extraversion: refers to the internal and external nature of the character.
2. Neuroticism: refers to emotional stability.
3. Psychoticism: refers to negative personality traits such as loneliness, coldness, hostility, and weirdness.
2. Big Five Personality Theory
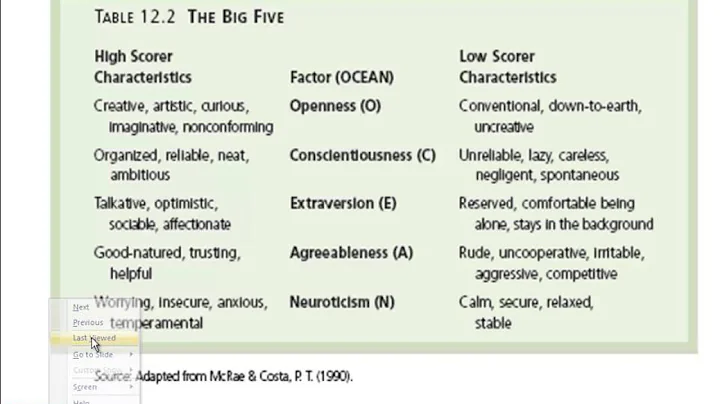
The Big Five Personality Theory was proposed by Costa and McCrae in the 1980s on the basis of predecessors. It is also called the five-factor model of personality. includes neuroticism or emotional stability, extraversion, openness, agreeableness and conscientiousness.

1. Neuroticism or emotional stability: Neuroticism reflects the individual's emotional regulation process and reflects the individual's tendency to experience negative emotions. Individuals with high neuroticism, that is, individuals with low emotional stability, tend to have psychological pressure, unrealistic ideas, excessive demands and impulses, and are more likely to experience negative emotions such as anger, anxiety, and depression. This dimension describes an individual's ability to withstand stress. Individuals with low neuroticism, that is, individuals with high emotional stability, tend to be peaceful, confident, and secure. Individuals with low emotional stability are prone to conflicts with others, directly destroying team harmony, and will encounter more resistance when getting along with others.
2. Extraversion: People with high extraversion like to interact with others, and are more gregarious, lively, optimistic, and good at social activities. is easy to interact socially with others and is willing to participate in discussions and put forward his own opinions. By showing more positive emotions, satisfaction with the team is also higher.
3. Openness: People with high openness are mostly creative, curious and observant. generally facilitates personal social interaction. People with certain traits tend to be more interested in novel things and can put their ideas into action in a timely manner.
4. Agreeableness: People with high agreeableness have a gentler personality, are supple and kind, easy to trust others and soft-hearted. is willing to take the initiative to establish friendship with others, avoid unnecessary disputes, and will not behave emotionally aggressively when getting along with others.Desire for social interaction with others and willingness to help others at any time.
5. Responsibility: also called conscientiousness. People with a high sense of responsibility are conscientious, organized, reliable and worthy of the trust of others. Because of this, the dimension of responsibility has always been an important indicator of personal performance. People with a high sense of responsibility are more determined to achieve goals, hope to challenge high-level performance, and are achievement-oriented in their work.
Research has shown that age is significantly negatively correlated with neuroticism and openness, and is significantly positively correlated with extraversion, agreeableness, and conscientiousness.
1. Among people under 60 years old, older individuals have lower neuroticism. Among people over 60 years old, older individuals have higher neuroticism.
2. Among people under the age of 50, older individuals have relatively higher levels of extraversion, and older individuals after the age of 50 have relatively lower levels of extraversion.
3. Overall, older individuals have relatively lower levels of openness, while older individuals have higher levels of agreeableness. Older individuals also have relatively higher levels of conscientiousness, but compared to the 40 to 49-year-old group, the conscientiousness of the group over 50 is relatively low.
4. There are certain differences in the Big Five personalities of men and women. Men are more conscientious than women, and women are more neurotic than men.
3. Big Six Personality Theory
Chinese scholar Zhang Jianxin and others proposed a six-factor model of personality after reviewing and summarizing previous research results, which is to add an interpersonal factor to the Big Five personality. This factor includes many "localized" personality constructs, showing the behavioral patterns and cultural connotations of how Chinese people "behave" in society, such as paying attention to interpersonal relationships, avoiding frontal conflicts, maintaining superficial harmony, and everyone having face, etc. .
In addition, some studies have shown that the lower correlation coefficients , , and between interpersonal factors and agreeableness factors indicate that there may be two interpersonal behavior patterns in Chinese society, and agreeableness is more indicative of a person's behavioral pattern. Whether passively being popular with others, interpersonality involves a behavioral pattern in which a person actively seeks to establish interactive exchange relationships with others. In other words, agreeableness is more related to how to "be a good person", while interpersonalness is more related to how to "be a good person" in a specific cultural situation.