what is heatstroke ? What are the symptoms of heatstroke? How to treat and provide first aid for heat stroke? How to prevent heat stroke?
![What is heat stroke? What are the symptoms of heatstroke? How to treat and provide first aid for heat stroke? How to prevent heat stroke? [Definition of heat stroke] Heat stroke should be considered in children who have been exposed to high temperature environments or have a hist - DayDayNews](https://cdn-dd.lujuba.top/img/loading.gif)
[Definition of heat stroke]
Heat stroke should be considered in children who have been exposed to high temperature environments or have a history of exposure to the scorching sun and experience sudden high body temperature, profuse sweating, dehydration accompanied by irritability, lethargy, muscle twitching, and impaired consciousness.
![What is heat stroke? What are the symptoms of heatstroke? How to treat and provide first aid for heat stroke? How to prevent heat stroke? [Definition of heat stroke] Heat stroke should be considered in children who have been exposed to high temperature environments or have a hist - DayDayNews](https://cdn-dd.lujuba.top/img/loading.gif)
[Overview of Heat Stroke]
When children spend a long time in a high temperature, high humidity environment or under direct sunlight, which leads to a series of symptoms such as imbalance of body temperature regulation function, disorder of water and salt metabolism, and damage to nervous system function, it is called heat stroke.
[The pathogenesis of heat stroke]
When the ambient temperature is higher than the body surface temperature, coupled with poor ventilation, the body's radiation and conduction convection heat dissipation methods are hindered. The external temperature instead raises the body temperature through radiation. At this time, sweating and evaporation are mainly relied on. However, when high temperature and high humidity environments exist at the same time, sweating, evaporation and heat dissipation are also seriously affected, resulting in a large accumulation of residual heat in the body, rapid rise in body temperature, causing excitement of the central nervous system, increased function of the endocrine system, and catabolism of proteins and sugars. Hyperactivity, increased heat production in the body, raising body temperature, and the two form a vicious cycle.
![What is heat stroke? What are the symptoms of heatstroke? How to treat and provide first aid for heat stroke? How to prevent heat stroke? [Definition of heat stroke] Heat stroke should be considered in children who have been exposed to high temperature environments or have a hist - DayDayNews](https://cdn-dd.lujuba.top/img/loading.gif)
[Symptoms of heat stroke]
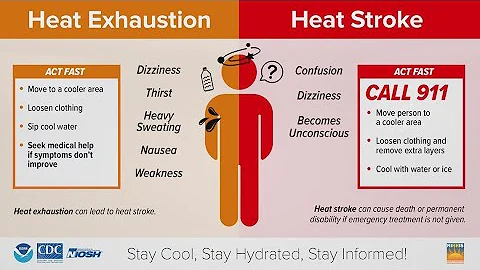
After long-term exposure to high temperature environment, symptoms such as headache, dizziness, thirst, excessive sweating, etc. will appear. The body temperature will be normal or slightly high at first, and continue to rise to above 38℃. In addition to the above symptoms, there will also be other symptoms. There may be flushing of the face, profuse sweating, burning skin, clammy limbs, etc. Without timely intervention, multiple organ failure may occur.
[Classification of heat stroke: premonitory heat stroke, mild heat stroke, severe heat stroke]
Premonitory heat stroke: after a certain period of activity in a high temperature environment, sweating a lot, thirst, dizziness, chest tightness, general fatigue, body temperature is normal or slightly elevated. High (37.5℃). If you can move to a ventilated place to rest in time and replenish water and salt appropriately, you can return to normal in a short time.
![What is heat stroke? What are the symptoms of heatstroke? How to treat and provide first aid for heat stroke? How to prevent heat stroke? [Definition of heat stroke] Heat stroke should be considered in children who have been exposed to high temperature environments or have a hist - DayDayNews](https://cdn-dd.lujuba.top/img/loading.gif)
Mild heatstroke: In addition to the aggravation of the above symptoms, the body temperature rises above 38°C, flushing of the face, burning skin, clammy skin all over the body, decreased blood pressure, increased pulse rate and other early manifestations of peripheral circulatory failure. If treated in time, it can be Recover within hours.
![What is heat stroke? What are the symptoms of heatstroke? How to treat and provide first aid for heat stroke? How to prevent heat stroke? [Definition of heat stroke] Heat stroke should be considered in children who have been exposed to high temperature environments or have a hist - DayDayNews](https://cdn-dd.lujuba.top/img/loading.gif)
Severe heat stroke: It is the most serious type of heat stroke. If not treated in time, it will be life-threatening.
![What is heat stroke? What are the symptoms of heatstroke? How to treat and provide first aid for heat stroke? How to prevent heat stroke? [Definition of heat stroke] Heat stroke should be considered in children who have been exposed to high temperature environments or have a hist - DayDayNews](https://cdn-dd.lujuba.top/img/loading.gif)
[Severe heat stroke can be divided into the following 4 types]
High fever type: manifested by sweating, thirst and fatigue, body temperature rising to 38--39℃, followed by excessive sweating, causing dysfunction of the hypothalamus and sweat glands, and skin inflammation No sweat, dry and burning, flushed face, accelerated breathing, rapid pulse, and the body temperature rises rapidly at this time to more than 41°C. The child is irritable, delirium , convulsions and coma. In severe cases, it may be complicated by cerebral edema, respiratory failure and important organs. Functional impairment;
circulatory failure type: high fever, thirst after sweating profusely, oliguria, nausea, vomiting, and shock . In severe cases, the skin is clammy, pale, and the blood drops. At this time, the body temperature drops instead. Children with mental changes or coma;
Heat spasm fever: the prominent manifestations are short-term twitching and painful spasms in the limb muscles, especially gastrocnemius , which will resolve spontaneously after a few minutes. In severe cases, the body muscles may also have twitching. . Normal body temperature or low fever. Clear consciousness;
Solar radiation type: Children who have been active under the scorching sun for a long time, and their heads are exposed to mid-infrared rays of the sun, causing congestion and edema of the meninges and brain tissue. The most prominent symptoms are dizziness, headache, dizziness, tinnitus , nausea and vomiting, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. The rectal temperature may not rise significantly.
[Heat stroke treatment]
1. Treatment of threatened heat stroke and mild heat stroke:
principle: every second counts, quickly get the patient out of the high-heat environment, quickly get out of the high-heat environment, take off his coat to rest in a cool place, drink mung bean soup or some salt-containing food Drinks, and give the patient anti-heat medicine, perform physical cooling, and apply cold compresses to the head and armpits. After the symptoms stabilize, a designated person will be designated to send the patient home or to the dormitory as appropriate.
2. Treatment of severe heat stroke:
Immediately move the patient Go to a cool and ventilated place to lie down, untie your clothes, blow on the air conditioner or electric fan, shower with cold water, or place ice packs on the head, neck, armpits, thighs, etc. to quickly cool down. If the person with heatstroke can drink water, let him drink cold salt water or other Drinks to replenish water and salt. After the symptoms are slightly better, you can go to the hospital for treatment under supervision. If there are serious conditions such as low blood pressure, collapse, spasm , convulsions, shortness of breath, unconsciousness, etc., you should contact a vehicle immediately and send the person to a nearby hospital for treatment.
![What is heat stroke? What are the symptoms of heatstroke? How to treat and provide first aid for heat stroke? How to prevent heat stroke? [Definition of heat stroke] Heat stroke should be considered in children who have been exposed to high temperature environments or have a hist - DayDayNews](https://cdn-dd.lujuba.top/img/loading.gif)
[First aid for heat stroke: move, apply, stimulate, soak, rub, take, transfer]
1. Move: quickly move the patient to a cool and ventilated place, and unbutton his clothes to facilitate breathing and heat dissipation.
2. Apply: You can apply a cold towel to the head or place ice packs or ice cubes on the patient's head, armpits, thighs, etc.
3. Promote: Place the patient in cold water and massage the skin of the limbs to dilate the blood vessels in the skin, accelerate blood circulation, and promote heat dissipation. If the body temperature drops to 38 degrees, cooling can be stopped.
4. Immersion: Place the patient's body at a 45-degree angle and immerse it in water of about 18 degrees, with the chest submerged as the degree. The water temperature should not be too low for the elderly, the infirm and patients with cardiovascular disease.
5. Wipe: Four people use towels to wipe around the patient's body at the same time to rub the skin red. Generally, rubbing for more than 15 minutes can lower the body temperature to 37-38 degrees. Most people whose brains are not seriously damaged can wake up quickly.
6. Take: Conscious patients or patients who wake up after cooling down can take mung bean soup, light salt water, etc. to relieve heat.
7. Transfer: Immediately transfer the patient to a nearby hospital, preferably by air-conditioned vehicle.
[How to prevent heatstroke]
1. Drink: Drink slowly when drinking, and don’t drink suddenly when you are thirsty. Drink warm water, not ice water, drink water regularly, do not wait until you are thirsty, drink boiled water, not raw water, drink fresh warm water, or drink warm water with light salt. boiling water.
2. Slow adaptation: Slowly adapt to changes in temperature, and slow down when engaging in outdoor activities.
3. Timely dissipation of heat: When it is too hot, you should shower your head and neck with water to let the water evaporate and help dissipate heat.
4. Pay attention to weight changes: Heat stroke may cause the body to gradually collapse over several days. If your weight plummets within a few days, you should pay more attention.
5. Wear a hat when going out: Wear a hat when going out in the summer to slow down the heat absorption of the head and neck, especially those who are bald or have little hair.
6. Wear light-colored clothes when going out: do not wear black or dark clothes. Don't go shirtless. To avoid absorbing more radiant heat, pure cotton clothes are the most breathable.
7. Eat more fruits and vegetables: Eat more melons and cooling vegetables: watermelon, winter melon, and bitter melon can diuretic, clear away heat and relieve summer heat.
8. Take frequent baths: Help sweat leave the body.
9. Ensure adequate sleep: arrange your work and rest time reasonably, and avoid excessive activities under strong sunlight at noon in the hot weather.
![What is heat stroke? What are the symptoms of heatstroke? How to treat and provide first aid for heat stroke? How to prevent heat stroke? [Definition of heat stroke] Heat stroke should be considered in children who have been exposed to high temperature environments or have a hist - DayDayNews](https://cdn-dd.lujuba.top/img/loading.gif)
Contributed by: Department of Critical Care Medicine, Jiujiang Maternal and Child Health Hospital Yin Dan
Content Review: Yang Bin
Editor: Dai Heng
Review: Tan Ruijuan