chronic nephritis develop into uremia ? Although chronic nephritis is closely related to uremia, and chronic nephritis is also the primary cause of uremia, clinically a large proportion of patients with chronic nephritis will not develop uremia.
1. Chronic nephritis and uremia
1. Symptoms and causes of chronic nephritis
Chronic nephritis is the abbreviation of chronic glomerulonephritis. It is a group of diseases consisting of multiple causes and pathological types, originating from glomerulus . Its basic clinical manifestations are proteinuria, hematuria , edema and hypertension . Different patients may have different symptoms. Some have a slow onset and slow progression. Some have acute attacks on a chronic basis, with or without varying degrees of renal failure subside. According to statistics, about 10% to 15% of chronic nephritis is caused by acute glomerulonephritis . Most patients with chronic nephritis have no history of acute nephritis , which may be caused by a variety of bacteria, viruses or protozoa through immune mechanisms, inflammatory mediators and non-immune mechanisms.
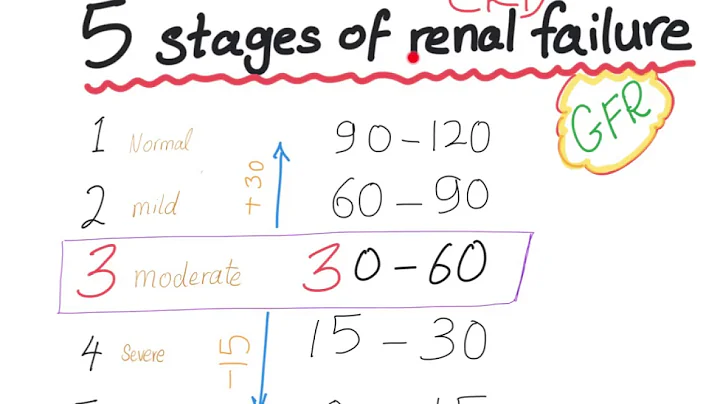
2. How far is it from chronic nephritis to uremia? Uremia is a clinical syndrome consisting of a series of symptoms and metabolic disorders that lead to irreversible decline in renal function until loss of function. It is not an independent disease, and is referred to as renal failure syndrome.
The cause of uremia is complex, and many factors can cause uremia. Chronic nephritis is one of the main reasons. Delayed treatment of chronic nephritis without appropriate treatment makes pathological chronic nephritis more dangerous. The condition of patients with chronic nephritis continues to worsen, which may eventually lead to the emergence of uremia. However, the transition from chronic nephritis to uremia is a complex process that is affected by a variety of factors.
(1) Pathological types
Among the common pathological types, mild mesangial proliferative nephritis has a good prognosis and is easy to alleviate; membranous nephropathy has a long history, but the disease develops slowly; severe mesangial proliferative nephritis, especially IgA Nephropathy , membranoproliferative nephritis and focal segmental sclerosis nephritis, poor prognosis, high chance of uremia.
In addition, patients with the following pathological changes are more likely to develop uremia: increased crescentic glomeruli; renal interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy; renal arteriosclerosis.
(2) Clinical manifestations
Patients with only hematuria or only a small amount of proteinuria, or hematuria with a small amount of proteinuria, and no other clinical symptoms have a better prognosis; 24-hour urine protein is greater than 1G, and the prognosis of patients with hypertension is poor. If you take lowering Antihypertensive drug treatment is effective, and the prognosis of patients with normal blood pressure is relatively good; those with renal damage develop to uremia faster.
(3) Treatment
If treatment is not timely or standardized, the damage to kidney function cannot be alleviated, which will accelerate the occurrence of uremia. Therefore, patients with chronic nephritis must go to the hospital in time for standardized treatment.
2. Face up to chronic nephritis
As a clinician, patients often ask, "When will my disease be completely cured?" In fact, chronic nephritis may not develop into uremia, but most other nephritis are difficult to cure (except acute infection glomerulonephritis can be cured), so mild nephritis does not necessarily require medication. Some nephritis requires lifelong medication, and the condition will develop slowly over time.
Therefore, the main purpose of our treatment is to slow down the progression of the patient's condition, try to maintain the stability of the patient's renal function, and avoid the deterioration of the patient's renal function, so that kidney disease will not affect the patient's life.
As for the patients themselves, we should adjust their mentality. Some patients with nephritis have mild symptoms but suffer from severe mental stress. In fact, the treatment of nephritis does not have a big impact on daily work and family life.
Healthy living is related to the prevention of uremia
1. Timely and standardized treatment of chronic nephritis
Early diagnosis, timely treatment and effective control of proteinuria, hematuria, edema and blood lipids are effective measures to prevent chronic nephritis from developing into uremia.
2, long-term periodic review
Chronic nephritis often has an insidious onset, and some patients only develop symptoms during the uremia stage, so regular physical examinations are very necessary.Necessary examinations include urine routine , blood routine , kidney function, blood electrolytes, blood pressure, double kidney ultrasound scan, etc.
3. Prevention of recurrence of chronic nephritis
Treatment of nephritis usually uses hormones and immunosuppressant . While some drugs control the condition, the incidence of side effects such as infection is also high. Infections such as pneumonia, tonsillitis , and diarrhea can cause nephritis to relapse or worsen. In these cases, it is necessary to promptly seek treatment at a nephrology department, and unauthorized use of drugs is strictly prohibited.
4. Adjust your lifestyle
Keep your mood comfortable, exercise appropriately, avoid overexertion, work and rest regularly, ensure adequate sleep, pay attention to personal hygiene, and avoid respiratory tract infections and intestinal infections. Adjust the diet structure to ensure high-quality protein (avoid large protein intake), high vitamins (except vitamin A), low phosphorus, low fat, and easy to digest diet.
5. Increase your health awareness, and uremia may be far away from you.
The process from chronic nephritis to uremia takes a long time. The symptoms in this process are not well expressed, but they are not traceable. Therefore, we must improve our health awareness, face up to chronic nephritis, conduct regular health examinations, and actively standardize treatment, which can prolong the process from chronic nephritis to uremia.
In other words, chronic nephritis is not as scary as imagined. Only a small number of nephritis patients will develop uremia, and many patients will not enter the uremia stage. Or some patients with nephritis will not develop uremia even if they enter the stage of renal insufficiency .