
Recently, some experts have reproduced the AlphaFold 2 model to make it easier for the public to use its functions.
This forked version is called OpenFold and uses the PyTorch framework. According to the PyTorch official website: "PyTorch is an open source machine learning framework that accelerates the path from research prototype to production deployment."

(Source: GitHub)
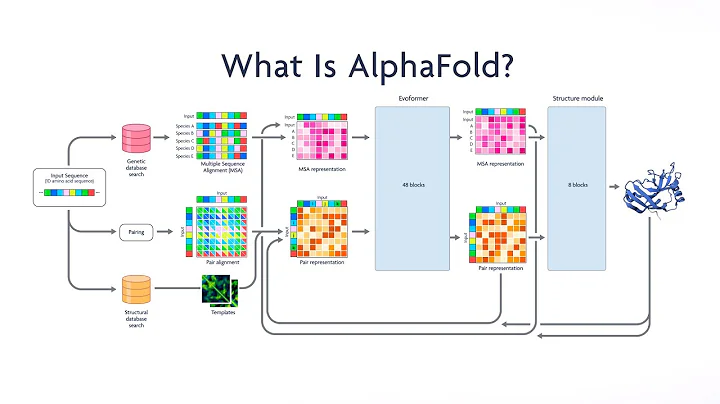
AlphaFold 2 is a deep learning system developed by the AI company DeepMind, which is best known for being used for predicting protein structure. This can be seen as a milestone event in the use of AI to promote scientific research.
Predictions of the protein structure are expected to yield a variety of benefits in the life sciences, such as accelerating the discovery of advanced drugs and better understanding of disease. AlphaFold 2 ranked first overall in the Critical Assessment of Protein Structure Prediction Technology (CASP) competition in November 2020 (its first-generation version also won the first place in the 13th CASP competition in December 2018 one). This is considered a major achievement in Computational Biology and a huge advance toward a grand challenge in biology that has existed for decades.
In July 2021, a paper related to using AlphaFold 2 to predict protein structure was published in Nature, titled "Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold". At the same time, DeepMind also released the proteome database to the public and made AlphaFold 2 open source.
However, the actual deployment of AlphaFold 2 is more difficult, and it is not friendly to ordinary developers in terms of hardware requirements, space occupation, and long download time. Therefore, relevant experts and the open source community are working hard to create a user-friendly version of AlphaFold 2.
Mohammed AlQuraishi, an assistant professor in the Department of Systems Biology at Columbia University, said that the trainable OpenFold model they built is the first complete public replica of AlphaFold 2 and has been open sourced on GitHub.

(Source: GitHub)
developers said: "OpenFold reproduces (almost) all features of the original open source inference code (v2.0.1). We have publicly released the model weights and training data, approximately 400,000 MSA (Measurement System Analysis, Measurement Systems Analysis) and PDB70 files. "
It is understood that the model weights are available through a script in the GitHub repository, and the MSA is provided by the Open Data Registry on AWS (Amazon Web Services, Amazon Web Services) RODA) hosting. All OpenFold code is based on the PyTorch environment, while AlphaFold 2 was developed for JAX workflows. Additionally, in addition to AlphaFold’s official parameters, OpenFold supports the use of developers’ own Colab notebooks for inference.
Then, it is worth mentioning that compared to the original AlphaFold 2, OpenFold even has advantages in inference speed and memory usage. For example, very long chain reasoning, faster short chain reasoning (about twice as fast as AlphaFold2), efficient alignment scripts, etc.
researchers said that the sequence structure of up to about 4600 amino acid residues can be obtained on 40GB A100, and can be further optimized. With the new customizable CUDA attention kernel, it consumes nearly four times less GPU memory than the FastFold kernel.
Comparing OpenFold and AlphaFold 2 based on the GDT_TS score on CAMEO's validation set, you can see from the scatter plot below that the accuracy of the two is very close. Even OpenFold is slightly better on average. The researchers explained that this may be due to their larger training set.

(Source: Twitter)
It is understood that OpenFold was trained on an A100 GPU for approximately 100,000 compute hours, but the final accuracy of 90% was achieved in only the first 3,000 compute hours. After the initial rapid increase, the accuracy gain slowed significantly, although it still climbed gradually, the researchers said. This has important implications for training OpenFold and AlphaFold 2 variants.
He also mentioned that the GPU used this time is the A100 released by NVIDIA, and he hopes to conduct training on lower-end GPUs in the future. Currently they have an AlphaFold-Gap option and should have a multimer version up and running soon (using AF2-multimer weights).
researchers also said that a related preprint article will be published soon, which contains a lot of details on training and research. And said: "Our OpenFold efforts are far from over. In fact, this is just the beginning. Please stay tuned for exciting news to follow."
Finally, protein folding is a problem that scientists have faced for decades. According to Wikipedia : "Protein folding is the physical process by which protein chains are translated into their native three-dimensional structure, usually the 'folded' conformation in which the protein becomes biologically functional."
Currently, its research is generally through "X-ray Techniques such as crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance are used for experimental determination. However, the use of these techniques is time-consuming and costly.
If it is possible to predict protein structure from the amino acid sequence alone, it will greatly help advance scientific research and may lead to comprehensive and rapid breakthroughs in medical and biological understanding.
Protein folding involves thermodynamics that determine the interatomic forces that determine the folded stable structure, the mechanisms and pathways by which proteins reach their final folded states extremely quickly, and how to predict the natural structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence.
Previously, researchers have also applied many computational methods to solve the problem of protein structure prediction, but except for small simple proteins, their accuracy is not close to experimental techniques, thus limiting their value. AI models such as OpenFold and AlphaFold 2 are expected to play an increasingly important role in protein folding problems.
-End-

Reference: https://twitter.com/MoAlQuraishi/status/1459188604723351552https://github.com/aqlaboratory/openfold#readmehttps://en.wikipedia. org/wiki/AlphaFold











![Manufacturing GMP-compliant iPSCs in closed and open systems [WEBINAR] - DayDayNews](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/maGgyWX_fhA/hq720.jpg?sqp=-oaymwEcCNAFEJQDSFXyq4qpAw4IARUAAIhCGAFwAcABBg==&rs=AOn4CLCLVKS0lvplIErvczV0SsT7ghBTJg)








