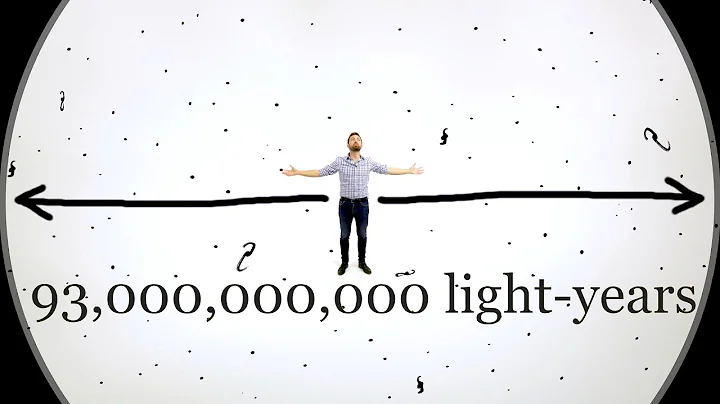's simple answer is that this question has nothing to do with speed. No matter how fast the speed is, it will not reach the boundary of the universe. If the spacecraft keeps flying, it will eventually not only fail to reach the boundary of the universe, but may even return to the starting point. Why is this happening?

It is necessary to do relevant science popularization here.
First of all, it is unrealistic for a spacecraft to fly faster than the speed of light , let alone 1 billion times the speed of light. In other words, the premise of the problem is unworkable and meaningless.
Einstein's 's special theory of relativity has long told us this, the speed of any object will not exceed the speed of light. Some people will definitely refute: Is the theory of relativity necessarily correct? Does relativity mean everything?
Any theory is moving forward under constant verification, and no theory is absolutely "right". After more than a hundred years of verification, the theory of relativity has not only not been overturned, but its status has become more and more stable. Therefore, it is right to question the theory of relativity, but you need to understand the basis for the birth of the theory of relativity, rather than simply and crudely opposing the theory of relativity.
Secondly, if you really want to travel across the universe, you don't need 1 billion times the speed of light, you just need to be infinitely close to the speed of light.
Purely theoretical analysis, when reaching the speed of light, there is no concept of time. No matter how far the distance is, for objects flying at the speed of light, they are always close at hand. The diameter of the observable universe is 93 billion light years. As long as the speed of light travels, you can reach the edge of the observable universe in an instant.
Although the speed of the spacecraft cannot reach the speed of light, as long as it is infinitely close to the speed of light, it will not take too long to travel through the observable universe.

Also, we don’t know the shape of the universe. Is the universe open or closed? Is it a plane or a sphere? The jury is still out. If the universe is a closed sphere, like our earth, this means that no matter which direction the spacecraft flies, it is impossible to fly out of the universe.
Just like no matter which direction we walk on the earth, we cannot go out of the universe, and we may eventually return to the starting point.
In other words, there is no so-called "inside" in the closed universe, everything is "inside". Without the outside, there is no so-called "border".
At the same time, according to the big bang theory of the universe, our universe does not have a so-called "center", or in other words, there are "centers everywhere" in the universe. How to understand this sentence?

needs to be understood from the definition of the observable universe. The diameter of the observable universe is 93 billion light-years, calculated with the Earth as the center. Since the universe is isotropic (the popular understanding is that no matter which direction you look, it is basically the same), so even if the diameter of the observable universe is measured on other planets, it is still 93 billion light-years.
For example, when measuring the diameter of the universe on Mars, Jupiter , or even the center of the Milky Way , the result is 93 billion light years. The place of measurement is the center of the universe.
The above point of view has an important premise: the speed of light cannot be exceeded. So to change the way of thinking, if you really want to fly out of the universe, as long as you can achieve faster than light speed. Purely theoretical analysis, once the speed exceeds the speed of light, you will fly out of the four-dimensional space and time , because super-light speed is prohibited in the four-dimensional space and time. When
reaches other time and space (such as high-dimensional time and space), does it mean that it has traveled through the universe?
Or maybe, this is another question. At present, it seems to be more of a science fiction issue.