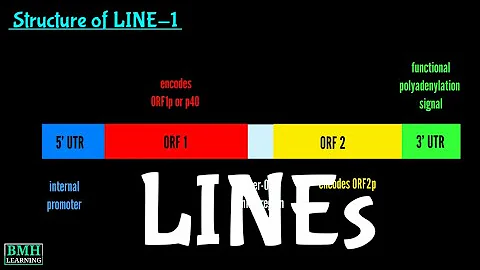
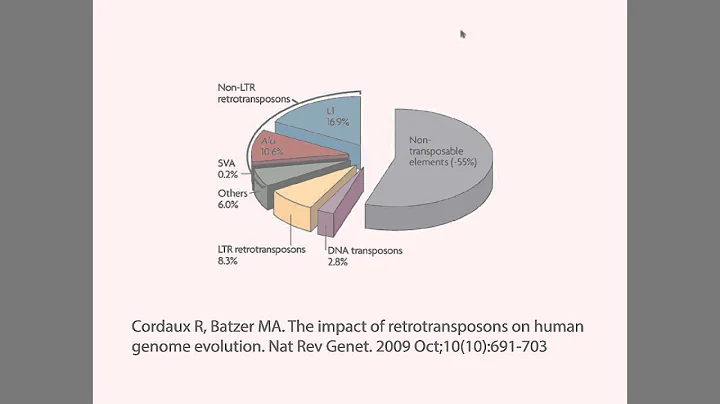
There are a large number of repetitive sequences in the human genome, including long interspersed nuclear element-1 (LINE-1) retrotransposons, human endogenous retroviruses (HERV), satellite repeat sequences, etc.
During normal development, repetitive sequences are mainly expressed during embryonic development and are suppressed in differentiated tissues [1]. During the occurrence and development of tumors, repetitive sequences abnormally express [2], and these abnormally expressed repetitive sequences RNA can be reversely transcribed into DNA, leading to the accumulation of cytoplasmic DNA in tumor cells, thus activating the cGAS-STING pathway to promote tumor progression [ 3].
This means that inhibits reverse transcriptase activity and may affect tumor progression and metastatic dissemination of . In fact, nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors are currently used clinically to treat HIV and HBV infections. So, can these drugs be used to treat tumors?
Recently, the research team led by David T. Ting and Benjamin D. Greenbaum of Massachusetts General Hospital affiliated with Harvard Medical School in the United States published the latest research [4] in the famous journal Cancer Discovery, which answered the aforementioned questions.
They used the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor lamivudine (3TC) to conduct functional research and mechanism exploration in colorectal cancer models, and conducted clinical trials in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, and found that 3TC has the ability to inhibit tumors. Progress potential of .

Screenshot of the paper's home page
In fact, the Ting team has previously studied the effect of the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors zalcitabine (ddC) and stavudine (d4T) in inhibiting the growth of colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Although these two drugs are also effective, these early nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors have serious side effects on patients [5]. This is obviously not suitable for clinical application.
In order to find reverse transcriptase inhibitor that is effective and has few side effects, this time they chose 3TC for testing. This is because studies have shown that 3TC has the potential to inhibit endogenous reverse transcriptase activity, and this drug is well tolerated by HIV and HBV patients..
Considering that the ability of tumor cells to migrate and avoid leaving their home base for spontaneous apoptosis (anoikis) is necessary for tumor metastasis. Therefore, the researchers first conducted a Transwell migration experiment and a soft agar colony formation experiment to explore the effect of 3TC on 10 colorectal cancer cell lines (p53 mutant: DLD1, HCT15, HT29, C2BBe1, LS123 and SW948; p53 wild type: HCT8, HCT116, LOVO and RKO) transfer effects. The results of
Transwell migration experiment showed that 3TC significantly inhibited the migration of DLD1, HCT15, C2BBe1, LS123 and RKO cell lines. It is not difficult to find that 3TC mainly acts on the p53 mutant cell line . Similar results were observed for soft agar colony formation experiments. Further, the researchers found that 3TC was effective in p53 mutant SW620 tumor-bearing mice, but was ineffective in p53 wild-type HCT116 tumor-bearing mice.

(L) and (M) are the tumor growth curves of p53 mutant (SW620) and wild-type (HCT116) colorectal cancer tumor-bearing mice respectively after being treated with 3TC or PBS.
After observing that 3TC was mainly effective on p53 mutant cell lines or tumor-bearing mice, the researchers then explored whether p53 had a direct effect on repeated sequence expression.
Researchers performed p53 immunoprecipitation sequencing in p53 mutant (SW620, DLD1) and wild-type (HCT116, HCT8) cell lines. Differential enrichment analysis found that satellite repeats (SAT) and LINE-1 were significantly different among the repeat sequences bound by p53 in the two cell lines. p53 mutant (SW620, DLD1) cell lines all have DNA-binding functional domain site mutations, suggesting that the loss of p53's DNA-binding function and the reduction of p53-repeated sequence interactions are related to .
Through RNA sequencing and chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, researchers found that the LINE-1 repeat subfamily L1PA2 is differentially expressed in p53 wild-type and mutant cell lines. Using RNA in situ hybridization technology, they found that the human satellite II (HSATII) satellite repeat sequence was significantly highly expressed in p53 mutant cell lines.

(C) Differential expression map of p53-bound repeat sequences in p53 mutant and wild-type cells.LINE, Statellite and ERV are the three main types of repeat sequences; (E) Representative and statistical diagrams of HSATII RNA in situ hybridization in p53 mutant and wild-type cells.
In view of preclinical studies finding that 3TC mainly acts on p53-mutated colorectal cancer cells, researchers conducted a phase II single-arm clinical trial (NCT03144804) of 3TC for the treatment of p53-mutated metastatic colorectal cancer. Trial enrollment conditions include refractory metastatic colorectal cancer with p53 mutations, progression or intolerance to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), oxaliplatin and irinotecan, and anti-EGFR therapy (RAS wild type); Patients aged ≥18 years with documented advanced disease (metastatic or unresectable) with histology or cytology who are incurable and have progressive disease on at least two systemic treatment regimens.
A total of 32 patients were eventually included in this study. The first nine patients took 3TC orally twice a day, 150 mg each time, in a 28-day cycle. After safety was assessed in 9 trial patients, the remaining 23 patients increased the dose to 600 mg each time. Tumor assessments were performed every 8 weeks until disease progression according to RECIST criteria or assessment of drug intolerance.
From the perspective of treatment effect, patients with stable disease (SD) had 8 (25%, Pts 7, 8, 11, 15, 20, 28, 31, 34), their median progression-free survival for 149 days. Among them, patient Pt 20 had the longest progression-free survival, reaching 230 days .
From the perspective of the safety of the treatment, no grade 5 adverse events occurred. Most of the adverse events in the tested patients were grade 3 (18/32, 56.3%), such as a decrease in the number of lymphocytes (11/32, 56.3%). 34.4%) etc. However, most grade 3 adverse events were caused by malignant tumor progression or systemic treatment before clinical trials. There were very few grade 3 adverse events related to 3TC treatment, including anemia (1/32, 3.1%) and diarrhea (2/32, 3.1%). 6.3%) etc.

(A) Clinical trial design; (B) Statistics of trial results of 32 patients.
To explore whether the efficacy of 3TC is related to the expression of repetitive sequences, the researchers evaluated samples from the patients before treatment.
They conducted RNA-seq on pre-treatment samples of 30 patients. The results showed that all patients tested highly expressed multiple repetitive sequence RNAs, and p53 mutations were present in the tumors. They used the immunohistochemical technique to evaluate the expression of LINE-1 protein in tumor samples of 28 patients, and found that the LINE-1 protein level in SD patients was significantly lower than that in PD patients, indicating that LINE-1 reverse transcriptase activity is sufficient in PD patients. Overcome the dose of 3TC used in the trial.
Since immunohistochemistry detects the LINE-1 protein in situ of the tumor, it can only reflect the primary tumor focus, but not the changes in tumor load throughout the patient's body. Therefore, the researchers used protein ultra-sensitive detection technology (Simoa) to detect peripheral Blood LINE-1 protein.
They found that SD patients had significantly lower plasma LINE-1 levels compared with PD patients, which may indicate differences in tumor burden, meaning that 3TC alone may not be able to combat tumors with high reverse transcriptase activity. In general, disease stabilization after 3TC treatment is related to low baseline levels of LINE-1 protein, but has nothing to do with repetitive sequence RNA expression or somatic retrotransposition. This indicates that 3TC plays a role in the repetitive sequence RNA life cycle before retrotransposition into the genome.

(G) Immunohistochemical detection of LINE-1 protein expression levels in tumor samples of test patients; (H) Serum LINE-1 protein levels of test patients.
In order to better understand the role of 3TC in colorectal cancer, the researchers used RNA sequencing to analyze paired pre-treatment and treatment samples from 13 test patients and found that the expression of repeated sequences was significantly reduced in patients with treated tumors. GO analysis found that the interferon response gene significantly upregulated .
It has been reported that interferon response may be related to sensing repetitive sequences of RNA and DNA [3]. The researchers hypothesized that 3TC treatment might change the content of repetitive sequence cDNA or RNA:DNA hybrid molecules formed by reverse transcription.They used quantitative immunofluorescence to detect the content of double-stranded DNA or RNA:DNA hybrid molecules in the cytoplasm of tumor cells. They found that the content of double-stranded DNA and in the p53 mutant (SW620, DLD1) cell line after 3TC treatment was significantly reduced, while RNA:DNA Hybrid molecule content significantly increases .

(E) and (F) are representative and statistical graphs of cytoplasmic dsDNA content and RNA:DNA hybrid molecule content of p53 mutant (SW620, DLD1) colorectal cancer cells treated with 3TC or DMSO using immunofluorescence detection respectively.
STING is known to be a recognition receptor for cytoplasmic DNA and RNA:DNA hybrid molecules. Knocking down STING in the DLD1 cell line can partially weaken the anti-migration effect of 3TC. These results indicate that 3TC may activate STING signaling by regulating the content of cytoplasmic nucleic acid molecules, thereby inhibiting cell migration .
Since the p53 mutation activates the expression of repeated sequences, thereby giving 3TC room to play its role, can lifting the silencing of repeated sequences and promoting their expression further enhance the efficacy or application scope of 3TC?
Considering that DNA methylation is one of the reasons for the silencing of repeated sequence expression [2], the researchers combined the DNA demethylation drug azacitidine (AZA) and nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors and found that The combination of and can promote cell necrosis, thereby reducing tumor growth, and has an effect in both p53 wild-type and mutant tumors.

Principle diagram of combined drug targeted regulation of repetitive sequence expression
So is this combination effect mediated by repeated sequences? Researchers focused on the aforementioned human satellite II (HSATII) satellite repeat sequence and used antisense nucleic acid LNA [5] to target HSATII and found that p53 mutant (SW620, DLD1) cell lines undergo necrosis, leading to the growth of cancer cells. suppressed. These results suggest that repeat-mediated interferon responses and cell necrosis are possible mechanisms of action of these drugs .
Researchers’ exploration of the mechanism of action of 3TC does not stop here. They treated the p53 mutant cell line with 3TC and conducted RNA sequencing analysis. The results found that in addition to the upregulation of innate immunity and interferon response genes mentioned above, DNA damage response-related genes were also significantly enriched.
In colorectal cancer cell lines treated with 5-fluorouracil/oxaliplatin (5FU/Oxa) combination and colorectal cancer patient samples after radiochemotherapy , researchers found that HSATII satellite repeat sequences were highly expressed. Therefore, researchers tried 3TC combined with 5FU/Oxa to treat tumor cells, and the results showed higher cytotoxicity of .

Volcano plot showing differentially enriched genes in p53 mutant cell lines after treatment with 3TC or DMSO. DDR: DNA damage response-related gene; IFN: Interferon response-related gene.
Overall, this study shows that colorectal cancer expresses abundant repetitive sequences with similar viral life cycles, and commonly used antiviral nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors are expected to become therapeutic drugs for intestinal cancer.
It is worth mentioning that the phase II single-arm clinical trial of 3TC in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer with p53 mutations suggests that 3TC treatment may benefit some patients, laying the foundation for subsequent NRITs combined with chemotherapy and other treatments for intestinal cancer.

Mechanism Schematic
In addition, this study also reminds us that the role of "dark matter" in the genome such as repeated sequences in the development and progression of tumors needs to be further explored, which will help us find more tumor targets and combination treatment strategies. .