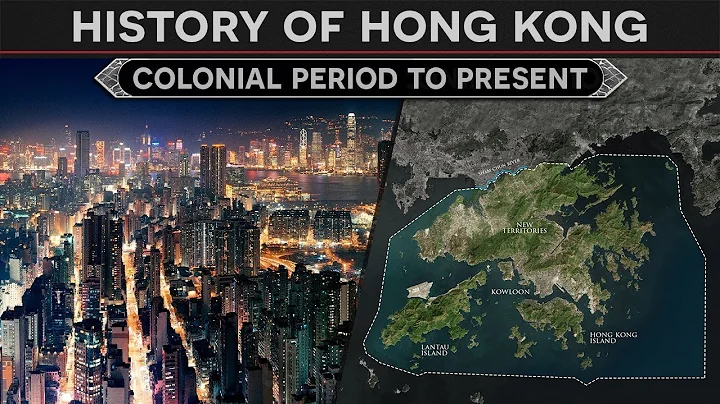
The return of Hong Kong refers to the historical event that the government of the People's Republic of China decided to resume the exercise of sovereignty over Hong Kong on July 1, 1997, and the government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland handed Hong Kong back to the People's Republic of China on July 1, 1997. .

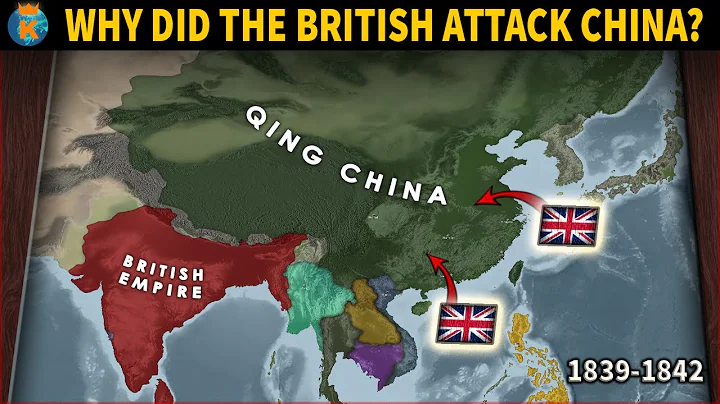
Britain began its colonial rule over Hong Kong during the First Opium War. At that time, the Qing government was defeated by the " Treaty of Nanjing" signed with the United Kingdom on August 29, 1842, and Hong Kong Island and duck legs were Europe was ceded to the UK. In October 1860, the Qing government was defeated again during the Second Opium War, and was forced to sign the "Beijing Treaty", which divided the Kowloon Peninsula (then known as the Kowloon Division 1 District) to the south of Boundary Street and Stonecutters European is handed over to the United Kingdom. In 1898, the Qing government signed the "Special Agreement to Expand the Boundary Site of Hong Kong" with the United Kingdom, leasing 230 large and small islands south of the Shenzhen River and north of Boundary Street to the United Kingdom, totaling 975.1 square kilometers of land, and The leased site is called " New Territories " and the lease term is 99 years. Beginning on July 1, 1898, and ending on June 30, 1997. Thus occupying the entire territory of Hong Kong.

In September 1982, the British government and the government of the People's Republic of China began negotiations on the future of Hong Kong. Although the Treaty of Nanjing and the Treaty of Beijing both referred to the permanent cession of Hong Kong Island, Ap Lei Chau, Kowloon south of Boundary Street and Stonecutters Island to the United Kingdom, the People's Republic of China refused to recognize the Treaty to Expand the Boundary Sites of Hong Kong. 》 and other related unequal treaties only recognized that Hong Kong was administered by the United Kingdom, not a British territory, and required the United Kingdom to return Hong Kong Island and Kowloon together with the New Territories. In 1997, the British government decided to return the sovereignty of Hong Kong to China, but at the same time strived to maintain British interests in Hong Kong.

After two years and 22 rounds of negotiations, China and the UK finally formally signed the "Sino-British Joint Declaration" on December 19, 1984, deciding that China would establish a special administrative region in Hong Kong from July 1, 1997. Re-exercise sovereignty and governance over Hong Kong Island, the Kowloon Peninsula, the New Territories and other lands south of Boundary Street .