tracks scientific research results and grasps the latest developments!
1 Major breakthroughs in shale gas exploration

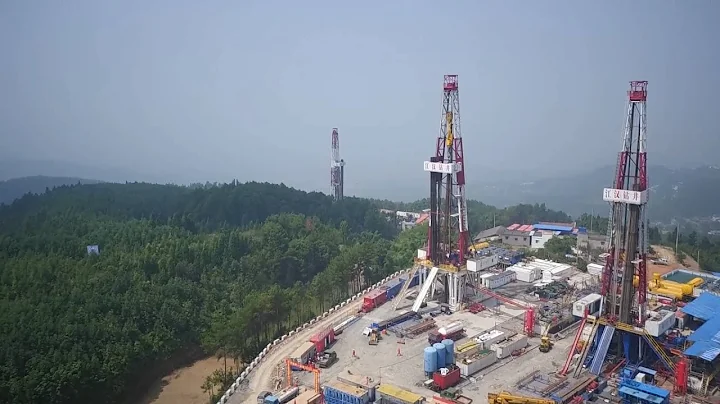
Image source: Sinopec
Sinopec The Xinye 1 well deployed in Qijiang, Chongqing has produced a trial production of 530,000 cubic meters of shale gas per day, marking the implementation of the Xinchang structure with 100 billion cubic meters of resources quantity. At this point, Sinopec's complex structural belt in the southeastern Sichuan basin margin "Xinchang South-Dongxi-Dingshan-Lintanchang" has formed an integrated contiguous area, with the overall resource volume reaching 1.19305 billion cubic meters. is Sinopec's successor to Fuling The second trillion-square-meter shale gas resource position discovered after the shale gas field will make an important contribution to ensuring my country's energy security.
According to reports, Well Xinye 1 was drilled to a depth of 5,756 meters. It is a deep shale gas risk exploration well deployed by Sinopec Exploration Branch in the Xinchang structure in Qijiang District, Chongqing. Geologically, the Xinchang structure belongs to the complex structural belt on the basin margin of southeastern Sichuan. Previous studies have shown that this structural belt has a large favorable area and large resources for ultra-deep shale gas. It is an important area for Sinopec to increase shale gas reserves and production.
After Sinopec made a major exploration breakthrough in the Fuling shale gas field in 2012, it turned its attention to the complex structural belt in the southeastern Sichuan Basin margin, established a deep shale gas technology research team, and continued to carry out technical research and development such as deep shale gas target evaluation. Deep shale gas volume fracturing technology has been formed, achieving 100% high-quality shale drilling encounter rate, and all fracturing equipment, tools and materials have been domestically produced, significantly reducing construction costs. In 2019, a strategic breakthrough was made in deep shale gas exploration. After that, we further promoted deep shale gas exploration and established a trillion-square-meter shale gas resource position.
Content source:
weixin://resourceid/blank
2 Revealing the identity of embryonic vascular endothelial progenitor cells
Recently, researcher Zeng Yi at the Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences and researcher Jing Naihe’s research team discovered that during embryonic development The identity of vascular endothelial progenitor cells updates the existing understanding of blood vessel formation and the establishment of the circulatory system, and also corrects the previously reported onset time of protein C receptor (Procr) expression in the embryo. At the same time, this study provides in vivo evidence to support the hypothesis that endothelial progenitor cells give rise to hematopoietic stem cells (hematopoietic endothelial cells). These findings provide molecular clues for the exploration of vascular endothelial progenitor cells and advance our understanding of vascular morphogenesis and the transformation of hematopoietic endothelial cells into hematopoietic cells.
Blood vessel growth and remodeling is a continuous physiological event that accompanies the development and homeostasis maintenance of all tissues, transports the required oxygen and nutrients, and plays an important role in maintaining the functions of various tissues in the body. crucial role. The vascular system is one of the earliest organs formed during the embryonic period. However, the identity of endothelial progenitor cells in the embryo is not yet clear. Previous research by Zeng Yi’s team revealed the specific protein marker Procr for adult vascular endothelial stem cells (Cell Research 2016). In order to explore whether Procr+ endothelial cells also exist in early embryonic development, the team used the ProcrmGFP-2A-LacZ reporter mouse model. Through whole embryo staining, combined with embryo in situ hybridization and analysis of spatial transcriptome data, the embryonic The starting time of Procr protein expression is E7.25 in the gastrula stage. The discovery of updates the previous study's view that "Procr is first expressed in the E13.5 main blood vessel." Through lineage tracing experiments, the team examined the characteristics of Procr+ endothelial progenitor cells and found that the vascular network formed by their progeny cells spreads throughout various tissues and organs of the embryo, and also contributes to the extraembryonic yolk sac and blood vessels in the placental tissue. The team then conducted single-cell transcriptome analysis on the progeny cells of early blood vessels (8.0-E8.5), mature blood vessels (E10.5) and lineage tracer-marked Procr+ cells and found that: they are located at the top of the lineage of vascular cell differentiation. The cell subpopulation (endothelial progenitor cell group) highly expresses Procr; the differentiation path starting from the endothelial progenitor cell group differentiates into the lineage branches of endothelial cells, and blood cells, suggesting that Procr+ endothelial progenitor cells may contribute to the development of blood cells. produce. This finding was further verified by Procr-CreER-mediated cell lineage tracing experiments.The research team found that specific killing of Procr+ progenitor cells in the early stages of development resulted in severe vascular development defects and embryonic death in embryos, yolk sacs and placental tissues, indicating that Procr+ endothelial progenitor cells are indispensable for the establishment of the early embryonic vasculature system. This study discovered the identity and molecular markers of embryonic endothelial progenitor cells, providing new clues for further understanding the mechanism of early embryonic vascular development and studying the transformation and differentiation of hematopoietic endothelial cells.
Content source:
https://www.cas.cn/syky/202206/t20220629_4839982.shtml
3 Researchers have developed a low-cost and high-efficiency hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst
Osteosarcoma is a tumor that is common in adolescents or children and is malignant. Characterized by high risk, strong invasiveness, and rapid disease progression, the exploration of the pathological mechanism and clinical treatment of osteosarcoma is a major problem facing the world. Analysis of clinical samples and public clinical databases shows that the expression of the chaperone protein TRiC is highly correlated with metastasis and overall survival rate of osteosarcoma. Patients with relatively low TRiC expression have a higher prognosis and survival rate and fewer recurrences. . These data indicate that the progression and prognosis of osteosarcoma are highly correlated with TRiC. TRiC mainly exists in the cytoplasm of eukaryotes, assisting ~10% of intracellular protein folding. It is a large bicyclic complex composed of 8 subunits , which plays a role in the synthesis, folding, transport and clearance of intracellular proteins. It plays an important role, and tumor cells will "hijack" the chaperone protein TRiC to maintain protein homeostasis under high protein synthesis rates. It is of great significance to find compounds that target the inhibition/interference of TRiC, but due to the huge structure of TRiC, the research work is full of challenges.
researcher Lai Ren’s research group at the Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Norway’s University of Oslo researcher Jin Yang’s research group, and Huazhong University of Science and Technology’s researcher Shengxia’s research group collaborated. Through virtual screening and in vitro experimental verification, they found that it comes from the highly toxic plant Curare. (Antiaris toxicaria Lesch.) natural compound coumarin β (anticarin-β) can directly interact with the key subunit CCT4 of the chaperone protein TRiC, inhibit TRiC activity, and subsequently inhibit the function of STAT3. Because TRiC is interfered with by compounds, the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes is blocked by coumarin β, resulting in abnormal autophagy in OS cells, disrupting cellular protein homeostasis and inducing apoptosis. The preclinical animal model of osteosarcoma revealed that coumarin β also has a good inhibitory effect on osteosarcoma, especially lung metastatic osteosarcoma, in vivo, without obvious systemic toxicity. These data support the potential of coumarin beta as a CCT4/TRiC inhibitor for the treatment of osteosarcoma. In addition, due to the important role of TRiC in maintaining protein homeostasis, the discovery of coumarin β, a natural compound that specifically targets TRiC, provides a powerful molecular tool for further research on TRiC and is important for understanding the role of TRiC in diseases such as tumors. of great significance.
Content source:
https://www.cas.cn/syky/202206/t20220621_4839003.shtml
4 Progress in industrial robot fault diagnosis research

Industrial robot experimental platform settings
Recently, The research team of the Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences has made progress in industrial robots. Research progress has been made in the field of fault diagnosis. proposed a fault diagnosis method for industrial robots under varying working conditions based on generative adversarial networks, which effectively improved the generalization ability of traditional data-driven industrial robot fault diagnosis algorithms.
industrial robots are known as "the crown jewel of the manufacturing industry", and their R&D and manufacturing applications are an important indicator of a country's technological innovation and high-end manufacturing levels. At present, industrial robot precision degradation and equipment failure are prominent problems, which have a huge negative impact on enterprise safety production and economic benefits. Currently, with the advancement of industrial Internet of Things and industrial big data technology, data-driven methods represented by machine learning, especially deep learning, have become a hot topic in industrial robot fault diagnosis research. However, during the actual operation of industrial robots, the rotation speed and load are continuously changing, which seriously affects the diagnostic performance of the data-driven method.
Content source:
https://www.cas.cn/syky/202206/t20220621_4838927.shtml
5 material metabolism simulation method of urban buildings
Progress in model construction
Rapid urbanization has increased the city's demand and use of building materials and waste have increased significantly in a short period of time, causing environmental problems. However, the existing material flow analysis (MFA) and geographical information system (GIS) coupling framework lacks the description of some key material metabolism processes in the various stages of building from construction, use to abandonment, resulting in the scale of material metabolism within the city. (especially construction material inflows and outflows) are underestimated.
In order to solve the above problems, Institute of Urban Environment of the Chinese Academy of Sciences based on collecting building data in Xiamen City and characterizing its three-dimensional morphological evolution characteristics, it defined and described the new construction, demolition, and demolition involved in the building life cycle . The four key processes of demolishing the old and building new ones (urban renewal) and damaged repairs are integrated into the existing MFA-GIS coupling framework to further evaluate and "restore" Xiamen in the process of urban development by buildings. The inflow and outflow of substances caused by metabolism.
Research shows that the existing framework lacks assessment of the generation of construction waste during the construction of new buildings (assessment that affects the outflow) and the assessment of material replacement caused by building maintenance during the use of the building (assessment that affects the inflow and outflow) As a result), the overall assessment results of material inflow and outflow were underestimated by nearly 40% and 65% respectively compared with the actual situation. This shows that the above-mentioned improved MFA-GIS coupling framework can more accurately describe and "restore" the material metabolism process of buildings, which helps to achieve accurate research and judgment on the building materials required by the city and accurate estimation of the amount of construction waste generated within the city. . At the same time, this framework can build a spatially explicit model through the "blessing" of geographic information systems to describe the spatial and temporal patterns and processes of urban material metabolism in detail, thereby helping municipal decision-making and management departments to formulate more targeted urban resource management and circular economy practices. Strategy.
The Institute of Urban Environment has established a series of spatiotemporal analysis frameworks, methods and models around the theme of urban metabolism, which can support high-precision spatiotemporal metabolic process simulations of urban buildings (this article), home appliances and solid waste, and create an urban metabolism "simulator" for the next step. "Lay a solid foundation.
Content source:
https://www.cas.cn/syky/202206/t20220629_4839827.shtml
cover image comes from the Internet
typesetting | Luobujuan
review | six blue-wing butterflies meteorite