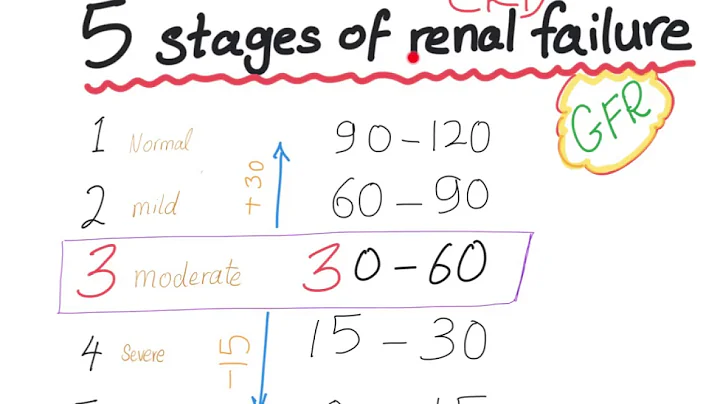
There is no doubt that physicians are concerned about the risk of disease progression in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). However, physicians have long relied on estimating glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) to predict the risk of disease progression in patients with CKD. So, are there any other risk prediction models with higher accuracy?
In May 2022, Ann Intern Med. released a risk equation study on the progression of CKD patients to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). This study showed that a 4-variable risk prediction equation was more effective in predicting whether patients with CKD would progress to ESKD within 2 years. These four variables are also relatively easy to obtain in clinical practice, namely age, gender, eGFR and urinary protein to creatinine ratio (UACR).
Study design
This is a cohort study based on data from the prospective Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort Study. There are seven research centers in total, all in the United States. The main purpose of this study was to compare the accuracy of 5 eGFR formulas and 4-variable risk prediction equations in predicting the progression of CKD patients to ESKD. It is reported that National Institutes of Health (NIH) has provided relevant support for this research.
Research results
A total of 3873 CKD patients were enrolled, aged between 21 and 74 years old (average age 58 years old), 55% of whom were male. Most of these patients are patients with mild to moderate CKD, with eGFR levels ranging from 20 to 70ml/min/1.73㎡. The study excluded patients who were receiving dialysis or immunosuppressive drugs, had a history of or planned organ transplant, cirrhosis, HIV infection, polycystic kidney disease or renal cell carcinoma.
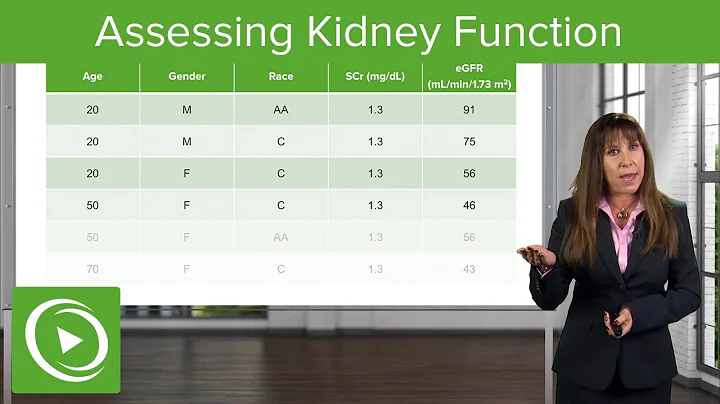
html The prediction results of the 15 eGFR prediction formulas and the 4-variable risk prediction equation are shown in the table below (Table 1).Table 1 Main results of the study

Researchers found that regardless of the eGFR formula used, the 4-variable risk prediction equation can more accurately predict the risk of disease progression in CKD patients. The sensitivity of the risk prediction equation was higher (>10%) than eGFR alone. The researchers believe that a 4-variable risk prediction equation should be used clinically instead of eGFR alone to predict the risk of disease progression in CKD patients.
In fact, continued revision of the eGFR equation is only a small step toward improving the efficiency and equity of kidney disease treatment. Recently, some large studies have confirmed that the risk prediction equation is also better than the eGFR formula alone in predicting the progression of CKD to ESKD within 5 years. Therefore, the researchers suggest that a 4-variable risk prediction equation should be used in the future to predict the risk of ESKD in CKD patients.
Reference:
1. Aguilar-Ramirez D, Herrington WG. In CKD, the Kidney Failure Risk Equation predicted 2-y risk for ESKD better than eGFR alone. Ann Intern Med. 2022 May;175(5):JC59.