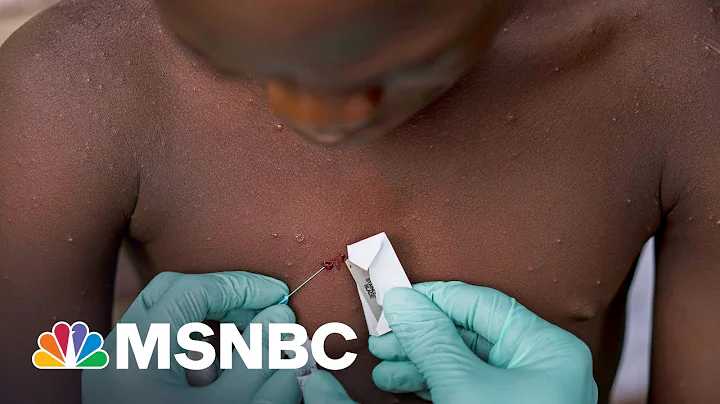
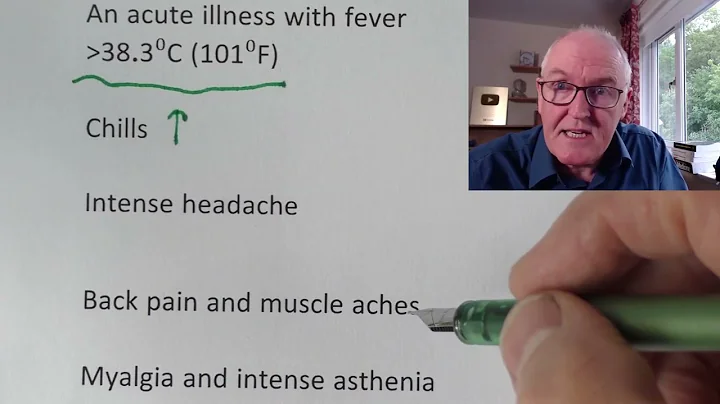
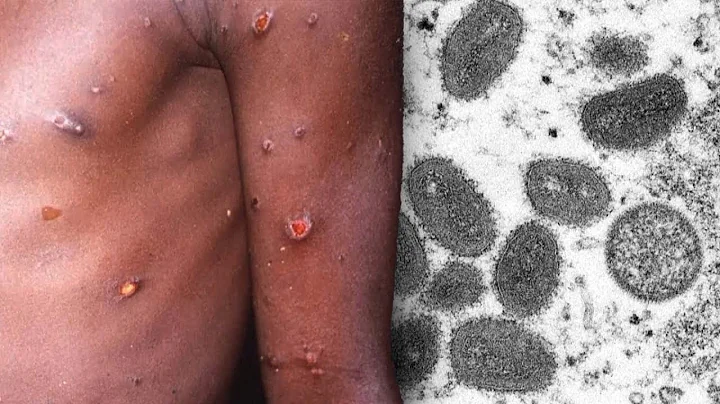
According to the official website of the World Health Organization , as of June 22, about 3,500 confirmed cases of monkeypox have been reported in 50 countries and regions around the world, most of which are from Europe. The reason for the abnormal spread of monkeypox is a mystery. Now scientists have discovered that the latest monkeypox virus mutates 6 to 12 times faster than expected, which may be the key to making it more contagious.

[Photo/Agencies]
The monkeypox virus strain that has emerged across the world in recent weeks may be evolving at an abnormally fast rate - making it more infectious than previous versions of the virus.
The monkeypox virus strain that has emerged across the world in recent weeks may be evolving at an abnormally fast rate - making it more infectious than previous versions of the virus.
Virus strains may evolve at an unusually rapid rate, making them more contagious than previous viruses.
This means that the virus, which is generally believed to spread by physical touch, contaminated surfaces or very close bodily contact could be able to spread in ways atypical to the tropical viruses normal patterns.
This means that it is generally believed to spread by physical touch, contaminated surfaces or very close bodily contact Monkeypox virus transmitted through surface or very close physical contact may be able to spread in ways that differ from the normal pattern of tropical viruses.
It would explain the recent global monkeypox update, where 201 cases have been detected across 25 U.S. states and Washington D.C., with over 3,500 cases detected worldwide in countries where the virus is not endemic.
201 cases have been detected in 25 U.S. states and Washington, D.C., and more than 3,500 cases have been detected in non-monkeypox virus-endemic areas worldwide.
Researchers, whose findings are pending official publishing in Nature Medicine, collected and studied 15 samples of the monkeypox virus for the study.
Researchers collected and studied 15 samples of monkeypox virus, and the research results were published in the journal Nature Medicine.
The research team restructured the viruses genetic information to find the number of changes the virus had undergone since this strain began its circulation.
The research team restructured the viruses genetic information to find the number of changes the virus had undergone since this strain began its circulation.
While the virus was detected recently in human populations, experts believe this strain of West African monkeypox first began its movement through the world in 2018.
While the virus was detected recently in human populations, experts believe this strain of West African monkeypox first began its movement through the world in 2018.
The strain first began spreading globally in 2018.
DNA viruses like monkeypox generally do not rapidly mutate like COVID-19 does.
DNA viruses like monkeypox generally do not mutate as rapidly as the new coronavirus.
The nature of the virus allows it to fix errors that emerge when it replicates, leaving much lower room for mutations to form - and in effect limiting the number of variants.
The nature of the virus allows it to fix errors that emerge when it replicates, leaving much lower room for mutations to form - and in effect limiting the number of variants. The likelihood of mutations is therefore low, which limits the number of times the virus can mutate.
When researchers did investigate this strain of the virus, they found that it had mutated between six to 12 times the generally believed rate for the virus.
When researchers did investigate this strain of the virus, they found that it had mutated between six to 12 times the generally believed rate for the virus. It is thought to be 6 to 12 times the virus mutation rate.
Why exactly this is cannot be determined, though the experts believe that this could be playing a role in how the virus has managed to storm the world this year. It has a certain effect, but the specific reason is not yet clear.
Source: Daily Mail Editor: Dong Jing
Source: China Daily Network