Author: Wang Fang
Introduction
Urticaria, commonly known as "urticaria" and "wind pimples" among the people, is a very common disease in dermatology clinics. 15% to 20% of people will have it at least once in their lifetime. Had urticaria once.
It is a localized edema reaction that occurs due to the dilation and increased permeability of small blood vessels in the skin and mucous membranes.

(Special type of urticaria: artificial urticaria)
Causes of urticaria
The causes of urticaria are complex, and most of them are difficult to find the exact cause. About 3/4 patients cannot find the cause, especially chronic urticaria.
So, what are the common factors that can cause urticaria?
1. Food
Fish, shrimp, crab, eggs, milk, etc. containing special proteins are common pathogenic factors; some plant foods, such as eggplant, bamboo shoots, spinach, etc.; and some food additives may also cause urticaria.
2. Inhaled substances
Various pollen, dust, animal dander, fungal spores, formaldehyde, gas, etc.
3. Infections
Bacterial infections, toxic infections, fungal infections and parasites; insect bites such as mites, fleas, bed bugs, etc.
4. Drugs
Penicillin, sulfa drugs, serum, vaccines, etc.
5. Physical and chemical factors
such as cold, heat, sunlight, friction and pressure and other physical and mechanical stimulation or certain chemical substances entering the human body.
6. Mental factors and endocrine changes
Mental stress, emotional impulse, menstruation, menopause, pregnancy, etc.
7. Internal medicine diseases
such as systemic lupus erythematosus, hyperthyroidism, rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis, gastroenteritis, stomatitis, etc.
8. Genetic factors
Some urticaria are related to genetic factors, such as hereditary familial urticaria syndrome, familial cold urticaria, etc.
The above points, including some other unspecified factors, lead to the activation and degranulation of mast cells in the body, releasing histamine, synthetic cytokines and inflammatory mediators, etc., causing vasodilation and increased vascular permeability, leading to dermal edema, thus forming The characteristic reaction of urticaria - wheal .
Clinical manifestations
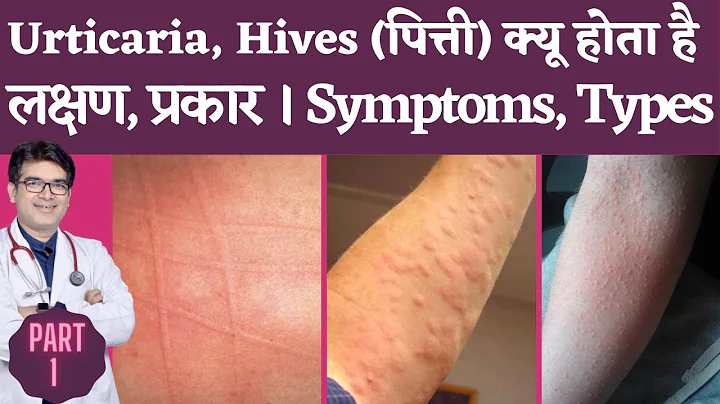
Characteristic clinical manifestations
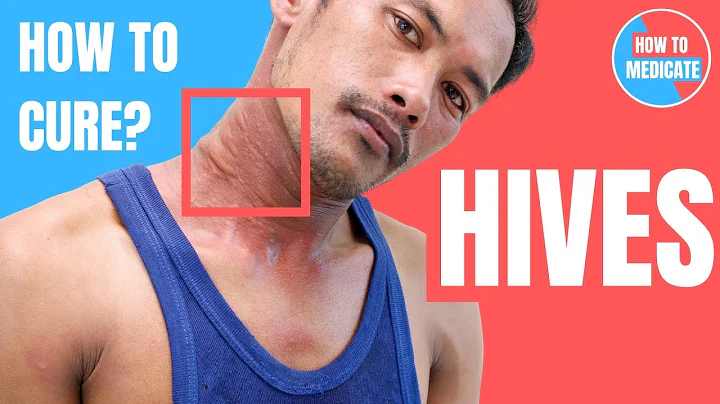
The characteristic clinical manifestations of urticaria are wheals , with various attacks, often accompanied by itching, and a few patients may be combined with angioedema . When
attacks, there is often itching of the skin first, and then red and white or skin-colored wheals appear. The size and shape of the wheals vary, and the onset time is uncertain. gradually spreads and can merge into sheets, accompanied by severe itching. A very small number of patients do not experience itching. Sometimes it is combined with angioedema, or bullae form on the surface of the wheal, or even bleeding.

Pictures come from the Internet
Some patients may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, headache, head fullness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. systemic symptoms such as chest tightness, pale complexion, accelerated heart rate, weak pulse, decreased blood pressure, and shortness of breath.
In extremely serious cases, acute laryngeal edema may lead to suffocation .
Features
The biggest feature of urticaria is that it can disappear on its own within a short period of time without leaving any traces . It simply comes and goes without a trace and disappears without a trace. It usually subsides within 2-24 hours, but new rashes are likely to recur, lasting days, months or even years.
If it can be cured in a short period of time, it is called acute urticaria; if it attacks at least twice a week and lasts for ≥ 6 weeks, it is called chronic urticaria. A small number of patients with chronic urticaria can also show intermittent attacks.
Diagnosis
Based on the typical symptoms and medical history, it is not difficult to diagnose urticaria and no more tests are required.
Acute patients can check blood routine to understand whether the onset is related to infection; chronic patients may consider related examinations if their condition is severe, the duration of the disease is long, or they have poor response to conventional doses of antihistamines. Such as blood routine, stool worm eggs, liver and kidney function, immunoglobulins, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, complement and various autoantibodies and other .
When necessary, allergen screening, food diary, autologous serum skin test (ASST) and Helicobacter pylori infection identification can be carried out to exclude and determine the role of related factors in the disease.
Treatment
The cause of this disease is unknown, the condition relapses, and the course is prolonged. Except for a few complications with respiratory or other systemic symptoms, most can be controlled or cured, and may self-heal.
Therefore, patients should actively cooperate with the treatment and have sufficient confidence in the cure.
Remove the cause and reduce the inducement
The fundamental treatment of this disease is to remove the cause. If some causes cannot be avoided, the predisposing factors should also be reduced as much as possible, especially physical urticaria, which is conducive to its natural regression.
A detailed medical history is the most important way to discover possible causes or triggers. For chronic urticaria clinically suspected to be related to various infections and/or chronic inflammation, when other treatments are resistant or ineffective, treatments such as anti-infection or inflammation control may be considered as appropriate, and some patients may benefit. For example, anti-Helicobacter pylori treatment has some effect on urticaria associated with Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis.
For patients with suspected food-related urticaria, patients should try to keep a food diary , look for possible foods and avoid them. After finding clear allergenic foods, taboos can achieve obvious results.
Medical treatment
For many patients with urticaria whose cause cannot be found, drug treatment can also achieve good results.
The main drugs currently used clinically to treat urticaria are second-generation non-sedating or low-sedating antihistamines, including cetirizine , levocetirizine, loratadine , di Loratadine, fexofenadine, avastin, ebastine, epinastine, mizolastine, olopatadine, etc. After the treatment is effective, gradually reduce the dose to achieve effective control of wheals.
In order to improve the quality of life of patients, the course of treatment for chronic urticaria is generally not less than 1 month, and can be extended to 3 to 6 months or longer if necessary.
Chlorpheniramine, diphenhydramine, doxepin, promethazine, ketotifen and other first-generation antihistamines are effective in treating urticaria, but due to central sedation, anticholinergic effects, etc. It has many adverse reactions and is now less used.
If the symptoms cannot be effectively controlled after 1 to 2 weeks of using second-generation antihistamines at regular doses, you can change the variety or increase the dose by 2 to 4 times, or combine it with first and second-generation antihistamines or anti-leukotriamines. ene drug to enhance efficacy.
In order to prevent drug resistance from long-term use of antihistamines, when a certain drug is ineffective, a different type of drug can be replaced.
acute urticaria caused by infection, anti-allergy and anti-infection treatment are also required. For acute, severe or urticaria accompanied by laryngeal edema, temporary intramuscular injection of dexamethasone or epinephrine can be used. Patients who fail to respond to any dose of antihistamines may be treated with oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, but long-term use should be avoided.
For severe autoimmune urticaria, intravenous immune globulin can be given.
For those who have relapsed for a long time and can identify the allergen, they can consider desensitization treatment, but desensitization treatment takes 2 to 3 years and requires a sufficient course of treatment.
Treatment of urticaria in special groups such as mothers and infants
In principle, try to avoid using antihistamines during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
However, if symptoms recur and seriously affect the patient's life and work, when antihistamines must be used for treatment, relatively safe and reliable drugs such as loratadine should be chosen.
Although it can enter breast milk, the amount that enters breast milk is very small and cannot reach the amount that can harm the baby. Nursing mothers do not need to wean their babies from taking this medicine.

The picture comes from the Internet
Moreover, Loratadine is available in a children's syrup form , which tastes better and can be used to treat urticaria in children.
References
[1] Immunology Group of the Dermatology and Venereology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Urticaria Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines (2014 Edition) [J]. Chinese Journal of Dermatology, 2014, 47(7):514-516.
[2 ] Zhao Zuotao, Hao Fei. Interpretation of Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Urticaria (2014 Edition) [J]. Chinese Journal of Dermatology, 2016, 49(6): 388-390.
(This article has been authorized by the author and is prohibited from being reproduced in any form)
Author introduction
Wang Fang, attending physician, has been practicing for 8 years and works in the Department of Dermatology and Venereology of Baoding First Hospital.
is good at: is good at the diagnosis and treatment of various common and frequent skin diseases and sexually transmitted diseases, such as neonatal acne, herpes zoster, tinea pedis, neurodermatitis, genital warts, etc., as well as the operation of various laser beauty equipment.
Regarding chickenpox and shingles infection during pregnancy, follow the public account "Mother and Infant Family Classroom"