There is a network around us all the time, such as telephone network, telegraph network, TV network, computer network, etc.; even there are many network systems inside our body, such as nervous system, digestive system, etc. The most typical representative is computer network, which is a combination of computer technology and communication technology.
1. Overview of computer networks

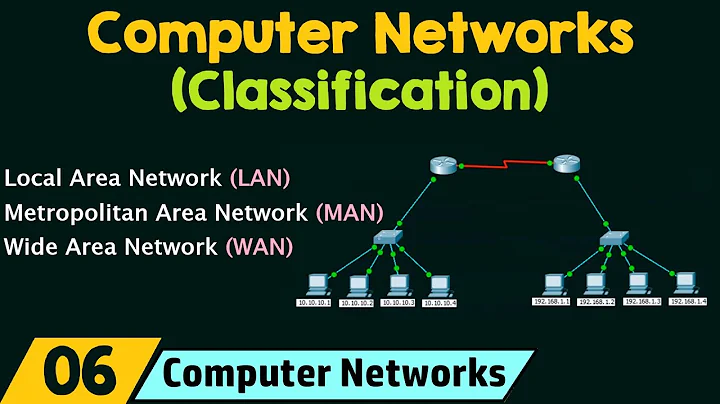
According to the scope of the network: wide area network (WAN), metropolitan area network (MAN), local area network (LAN);
according to network users: public network , private network .

TCP/IP four-layer model and OSI architecture comparison:

The layers are independent of each other;
Each layer needs to be flexible enough ;
is completely decoupled between each layer.

Rate: bps=bit/s Delay: sending delay, propagation delay, queuing delay, processing delay Round trip time RTT: one round trip of data packets in end-to-end communication time.
2. Physical layer
The role of physical layer : connect different physical devices and transmit bit streams. This layer provides a reliable physical medium for transmitting data to upper layer protocols. Simply put, the physical layer ensures that raw data can be transmitted over various physical media.
physical layer equipment:
repeater [Repeater, also called amplifier ]: regeneration signal of the same LAN; the network segments of the two ports must be the same protocol; 5-4-3 regulations: in 10BASE-5 Ethernet, the most 4 repeaters are connected in series, and only 3 of the 5 segments can connect to the host;
hub : regeneration and amplification signals of the same LAN (multi-port repeater); half-duplex, cannot isolate conflict domains and cannot isolate broadcasts area.
The basic concept of channel: A channel is a medium that transmits information in one direction. A communication circuit includes a sending channel and a receiving channel.
simplex communication channel: only one direction of communication, no feedback channel in the opposite direction;
half-duplex communication channel: both parties can send and receive information, but cannot send or receive at the same time;
full-duplex communication channel : Both parties can send and receive at the same time.
3. Data link layer
.1 Overview of the data link layer
The data link layer provides services to the network layer based on the services provided by the physical layer. Its most basic service is to make data from the network layer reliable. transmitted to the target machine network layer of adjacent nodes. The data link layer provides reliable transmission over unreliable physical media.
The functions of this layer include: physical address addressing, data framing, flow control , data error detection, retransmitting , etc.
Important knowledge points about the data link layer:
The data link layer provides reliable data transmission for the network layer;
The basic data unit is the frame;
The main protocol: Ethernet protocol;
Two important device names: bridges and switches .
is encapsulated into frames: "Frame" is the basic unit of data in the data link layer:

Transparent transmission: "Transparent" means that even if the control characters are in the frame data, they should be treated as if they do not exist. That is, add the escape character ESC before the control character.

.2 Error monitoring at the data link layer
Error detection: parity check code, cyclic redundancy check code CRC
Parity check code – Limitations: When two bits are wrong, the error cannot be detected.
cyclic redundancy check code: a fixed-digit check code is generated based on the transmitted or saved data.
.3 Maximum Transmission Unit MTU
Maximum Transmission Unit MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit), the data frame of the data link layer is not infinite, and the length of the data frame is limited by the MTU.
Path MTU: Determined by the minimum value of the MTU in the link.

.4 Detailed explanation of Ethernet protocol
MAC address: Each device has a unique MAC address, a total of 48 digits, expressed in hexadecimal.
Ethernet protocol: It is a widely used LAN technology and a protocol applied to the data link layer. Using Ethernet can complete the data frame transmission of adjacent devices:

LAN classification:
Ethernet Ethernet IEEE802. 3:
Ethernet's first widely deployed high -speed LAN
Ethernet data rate fast L1 Ethernet hardware is cheap, and the cost of network cost is low.
Ethernet frame structure:
Type: Make upper layer protocol (2 bytes)
htmmmml3htmmm L12Destable address and source address: MAC address (6 bytes each)
data: packet of encapsulated upper layer protocol (46~1500 bytes)
CRC: cyclic redundancy code (4 bytes)
Ethernet shortest frame: Ethernet frame shortest 64 bytes; the Ethernet frame is 18 bytes except for the data part; the minimum data is 46 bytes;
MAC address (physical address, LAN address)
MAC address length is 6 bytes, 48 bits;
MAC address is unique, each network Adapter corresponds to a MAC address;
usually uses hexadecimal notation, each byte represents a hexadecimal number, connected with - or:;
MAC broadcast address: FF-FF-FF-FF-FF- FF.
4. Network layer
The purpose of the network layer is to realize transparent transmission of data between two end systems. Specific functions include addressing and routing, connection establishment, maintenance and termination, etc. data exchange technology is message exchange (basically replaced by packets): a store-and-forward method is used, and the data exchange unit is a message.
There are many protocols involved in the network layer, including the most important protocol, which is also the core protocol of TCP/IP-IP protocol. The IP protocol is very simple and only provides unreliable, connectionless transmission services. The main functions of the IP protocol are: connectionless datagram transmission, datagram routing and error control.
and IP protocols are used in conjunction with the address resolution protocol ARP, the reverse address resolution protocol RARP, the Internet message protocol ICMP, and the Internet group management protocol IGMP. We will summarize the specific protocols in the next section. The key points about the network layer are:
The network layer is responsible for routing data packets between subnets.In addition, the network layer can also implement functions such as congestion control and Internet interconnection; the basic data unit of
is IP datagram; the main protocols included in
IP protocol (Internet Protocol);
ICMP protocol (Internet Control Message Protocol. Internet Control Message Protocol);
ARP protocol (Address Resolution Protocol, address resolution protocol);
RARP protocol (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol, reverse address resolution protocol).
Important equipment: router.

Router related protocols

 .1 Detailed explanation of IP protocol
.1 Detailed explanation of IP protocol
IP Internet Protocol is the core protocol of the Internet network layer. The emergence of the virtual Internet network: the actual computer network is intricate; physical devices shield the differences between physical networks by using the IP protocol; when the hosts in the network are connected using the IP protocol, there is no need to pay attention to the network details, thus forming the virtual network . The

IP protocol turns a complex actual network into a virtual interconnected network; and solves the problem of datagram transmission paths in the virtual network.

Among them, the version refers to the version of the IP protocol, occupying 4 bits, such as IPv4 and IPv6; the header length indicates the IP header length, accounting for 4 bits, with a maximum value of 15; the total length indicates the total length of the IP datagram, occupying 16 bits, the maximum value The numerical value is 65535; TTL indicates the lifespan of the IP data message in the network, accounting for 8 bits; the protocol indicates what protocol the specific data carried by the IP data is, such as TCP, UDP.
 .2 IP protocol forwarding process
.2 IP protocol forwarding process
 .3 IP address of The subnet divides
.3 IP address of The subnet divides 
A (8 network number+24 host number), Class B (16 network number +16 host number), Class C (24 network number +8 +8 +8 Host number) can be used to identify a host or router in a network, Class D addresses are used as group broadcast addresses , Class E are reserved addresses.

 .4 Network address translation NAT technology
.4 Network address translation NAT technology
is used in private networks where multiple hosts access the Internet through a public IP, which slows down the consumption of IP addresses, but increases the complexity of network communication .
NAT working principle:
replaces the IP address of the IP datagram sent from the intranet with the legal public IP address owned by NAT server , and records the replacement relationship in the NAT conversion table;
returns the IP data from the public Internet report, retrieve the NAT translation table based on its destination IP address, replace the destination IP address with the retrieved internal private IP address, and then forward the IP datagram to the internal network.
 .5 ARP protocol and RARP protocol
.5 ARP protocol and RARP protocol
Address Resolution Protocol ARP (Address Resolution Protocol): Provides dynamic mapping from the IP address of the network card (network adapter) to the corresponding hardware address. The network layer 32-bit address can be converted into the data link layer MAC 48-bit address.
ARP is plug-and-play. An ARP table is automatically created and does not require configuration by the system administrator.

RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol) protocol refers to the reverse address resolution protocol, which can convert the data link layer MAC 48-bit address into a network layer 32-bit address.
 .6 Detailed explanation of ICMP protocol
.6 Detailed explanation of ICMP protocol
Internet Control Message Protocol (Internet Control Message Protocol) can report error messages or abnormal situations. ICMP messages are encapsulated in IP datagrams.

ICMP protocol application:
Ping application: troubleshooting network faults;
Traceroute application: can detect the path that IP datagrams take in the network.
 .7 Network layer routing overview
.7 Network layer routing overview
Requirements for routing algorithms: correct and complete, computationally simple as possible, adaptable to changes in the network, stable and fair.
Autonomous system AS: refers to a network device group under a management organization. The AS internal network is autonomously managed and provides one or more external entrances and exits. The routing protocol within the autonomous system is an internal gateway protocol, such as RIP, OSPF, etc.; autonomous system The external routing protocol is the external gateway protocol, such as BGP.
static routing : manual configuration, high difficulty and complexity;
dynamic routing :
link state routing algorithm LS: sending information to all neighbor routes converges quickly; global routing algorithm, when each router calculates the route, It is necessary to construct the entire network topology diagram; use the Dijkstra algorithm to find the shortest path from the source end to the destination end network; Dijkstra (Dijkstra) algorithm
distance-vector routing algorithm DV: sending information to all neighbor routes converges slowly and may exist Loop; the basis is the Bellman-Ford equation (referred to as the B-F equation);
 .8 RIP protocol of the interior gateway routing protocol
.8 RIP protocol of the interior gateway routing protocol
Routing Information Protocol RIP (Routing Information Protocol) [ application layer ], distance-vector based routing algorithm , the smaller AS (autonomous system) , suitable for small networks; RIP messages are encapsulated into UDP datagrams.
RIP protocol characteristics:
RIP uses hop count when measuring paths (each router maintains a record of the distance from itself to every other router); the cost of
RIP is defined between the source router and the destination subnet; the network diameter of
RIP is restricted No more than 15 hops;
exchanges all information with the neighbor, 30 active times (broadcast).
 .9 Internal gateway routing protocol OSPF protocol
.9 Internal gateway routing protocol OSPF protocol
Open Shortest Path First protocol OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) [network layer], a routing selection algorithm based on link status (i.e., Dijkstra algorithm), larger-scale AS, suitable for large-scale network, directly encapsulated in IP datagrams for transmission.
OSPF protocol advantages:
is secure;
supports multiple paths with the same cost;
supports differentiated cost measurement;
supports unicast routing and multicast routing;
hierarchical routing. Comparison between
RIP and OSPF (the routing algorithm determines its nature):

 .10 BGP protocol of the external gateway routing protocol
.10 BGP protocol of the external gateway routing protocol
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Border Gateway Protocol [Application layer]: It is a protocol that runs between ASs. Looking for an Good routing: All information is exchanged for the first time, and only the changed parts are exchanged in the future. BGP encapsulates the TCP message segment.
5. Transport layer
The first end-to-end, that is, the host-to-host level. The transport layer is responsible for segmenting upper layer data and providing end-to-end, reliable or unreliable transport. In addition, the transport layer also handles end-to-end error control and flow control issues. The task of the
transport layer is to make optimal use of network resources based on the characteristics of the communication subnet , provide the functions of establishing, maintaining and canceling transmission connections between the session layers of the two end systems, and is responsible for end-to-end reliable data transmission. At this layer, the protocol data unit of information transmission is called a segment or message.
The network layer only transmits the data packets sent by the source node to the destination node according to the network address, while the transport layer is responsible for reliably transmitting the data to the corresponding port.
Key points about the network layer:
The transport layer is responsible for segmenting the upper layer data and providing end-to-end, reliable or unreliable transmission, as well as end-to-end error control and flow control issues;
The main protocol included: TCP protocol (Transmission Control Protocol, Transmission Control Protocol), UDP Protocol (User Datagram Protocol, User Datagram Protocol);
Important equipment: gateway.


.1 Detailed explanation of UDP protocol
UDP (User Datagram Protocol: User Datagram Protocol), is a very simple protocol,

UDP protocol characteristics:
UDP is a connectionless protocol;
UDP cannot guarantee reliable delivery of data;
UDP is for message transmission.
UDP has no congestion control;
UDP has very little header overhead.
UDP datagram structure:
header: 8B, four fields/2B [source port | destination port | UDP length | checksum] data field: application data

.2 TCP protocol detailed explanation
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol: Transmission Control Protocol), It is a very complex protocol in computer networks.

TCP protocol Function:
Corresponding layer message;
is for the application layer to implement reuse and decomposition;
implements end -to -end traffic control;
- plunger control;
transfer layer address;
The message is subject to error detection (error detection in both header and data parts);
realizes end-to-end reliable data transmission control between processes. Characteristics of the
TCP protocol:
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol;
TCP is a byte stream-oriented protocol;
TCP has two ends, namely point-to-point communication ;
TCP provides reliable transmission services ;
TCP protocol provides full-duplex communication ( Each TCP connection can only be one-to-one);
.2.1 TCP message segment structure:
Maximum message segment length: the maximum length of the application layer data encapsulated in the message segment.

TCP header:
Serial number field: The TCP sequence number is to number each byte of each application layer data
Confirmation sequence number field: The byte sequence number expected to receive data from the other party, that is, the byte corresponding to this sequence number has not been received. Identified by ack_seq;
TCP segment has a minimum length of 20B and a maximum length of 60 bytes.But the length must be an integer multiple of 4B
The role of TCP tags:

.3 Basic principles of reliable transmission
Basic principles:
Unreliable transmission channels What may happen in data transmission: bit errors , out of order, retransmitted, lost
Measures taken to achieve reliable data transmission based on unreliable channels:
Error detection: Using encoding to achieve bit error detection during data packet transmission Confirmation: The receiving direction feeds back the receiving status to the sender Retransmission: The sender resends the data that the receiver did not receive correctly Data sequence number: ensures that data is submitted in order. Timer: solves the problem of data loss;
stop waiting protocol : is the simplest reliable transmission protocol, but the channel utilization rate of this protocol is not high.
continuous ARQ (Automatic Repeat reQuest: automatic retransmission request) protocol: sliding window + cumulative confirmation, which greatly improves channel utilization. The reliable transmission of
.3.1TCP protocol
is based on the continuous ARQ protocol. In some cases, the retransmission efficiency is not high, and some bytes that have been successfully received will be repeatedly transmitted.
.3.2 TCP protocol flow control
flow control: Let the sender not send too fast. The TCP protocol uses a sliding window to achieve flow control.

.4 TCP protocol congestion control
The difference between congestion control and flow control: flow control considers the control of point-to-point traffic, while congestion control considers the entire network and is a global consideration. Congestion control method: slow start algorithm + congestion avoidance algorithm.
slow start and congestion avoidance:
[slow start] the congestion window grows exponentially from 1;
enters [congestion avoidance] when it reaches the threshold and becomes +1 growth;
[timeout], the threshold becomes half of the current cwnd (cannot be 2 );
and then start from [Slow Start], the congestion window grows exponentially from 1.

Fast retransmission and fast recovery:
The sender receives 3 redundant ACKs in a row and executes [fast retransmission] without waiting for the timer to expire;
executes [fast recovery], and the threshold becomes half of the current cwnd (cannot 2 ), and enter [Congestion Avoidance] from this new ssthresh point.

.5 Three-way handshake of TCP connection (important)
TCP three-way handshake usage instructions:

Frequent interviewer: Why is the three-way handshake needed?
The first handshake: the client sends a request, at this time the server knows that the client can send;
The second handshake: the server sends a confirmation, at this time the client knows that the server can send and receive;
The third handshake: the client sends a confirmation, at this time The server knows that the client can accept it.
establishes a connection (three-way handshake):
the first time : the client sends a connection request segment to the server and establishes a connection request control segment (SYN=1), indicating that the sequence number of the first data byte of the transmitted message segment is x, this sequence number represents the sequence number of the entire message segment (seq=x); the client enters SYN_SEND (synchronous sending state);
the second time : the server sends back a confirmation message segment, agreeing to establish a new connection confirmation segment ( SYN=1), confirm that the sequence number field is valid (ACK=1), the server tells the client that the sequence number of the segment of the message is y (seq=y), indicating that the server has received the client's message segment with the sequence number x and is ready to accept it The client's message segment with serial number x+1 (ack_seq=x+1); the server enters SYN_RCVD from LISTEN (synchronous reception status);
The third time : The client confirms the same connection to the server. Confirm the sequence number field Valid (ACK=1), the sequence number of the client's message segment this time is x+1 (seq=x+1), and the client expects to receive the message segment with the server's sequence number y+1 (ack_seq=y+1) ; When the client sends an ack, the client enters the ESTABLISHED state; when the service receives the ack sent by the client, it also enters the ESTABLISHED state; the third handshake can carry data;

.6 Four waves of TCP connection (important)
release Connection (waved four times)
The first time : The client sends a release connection message segment to the server. The sender data is sent and the connection is requested to be released (FIN=1). The sequence number of the first data byte transmitted is x ( seq=x); the client status changes from ESTABLISHED to FIN_WAIT_1 (terminate waiting 1 state);
second time : the server sends a confirmation segment to the client, confirming that the field number field is valid (ACK=1), and the data sequence number transmitted by the server is y ( seq=y), the server expects to receive the customer data sequence number x+1 (ack_seq=x+1); the server status changes from ESTABLISHED to CLOSE_WAIT (closed waiting); after the client receives the ACK segment, it changes from FIN_WAIT_1 to FIN_WAIT_2;
third Time : The server sends a release connection message segment to the client, requesting to release the connection (FIN=1), and confirms that the field number segment is valid (ACK=1), indicating that the server expects to receive the customer data sequence number x+1 (ack_seq=x+1) ; Indicates that the first byte sequence number transmitted by itself is y+1 (seq=y+1); the server status changes from CLOSE_WAIT to LAST_ACK (last confirmation status);
fourth time : the client sends a confirmation segment to the server to confirm the font size The segment is valid (ACK=1), which means the data sequence number transmitted by the client is x+1 (seq=x+1), which means the client expects to receive the server data sequence number y+1+1 (ack_seq=y+1+1); the client The end state enters Time_wait from Fin_WAIT_2, wait for 2MSL to enter the closed state; after receiving the last ACK, the server enters the closon by Last_ack;


Why do you need to wait for 2msl?
The last message is not confirmed;
ensures the sender's ACKKKKKKKKKKKKKKA Be able to Reach the receiver;
- MSL is not received within the time, the receiver will resend;
ensures that all messages currently connected have expired.
6. Application layer
provides an interface for accessing network services for the operating system or network applications. Focus on the application layer:
The basic unit of data transmission is the message; the main protocols included in
are: FTP (File Transfer Protocol), Telnet (Remote Login Protocol), DNS ( Domain Name Resolution Protocol), SMTP (Mail Transfer Protocol), POP3 protocol (Post Office Protocol), HTTP protocol (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol).
.1 DNS detailed explanation
DNS (Domain Name System: Domain Name System) [C/S, UDP, Port 53]: Solve the problem of complex and difficult to remember IP addresses, store and complete the mapping of domain names to IP addresses of hosts within your jurisdiction .The order of domain name resolution of
:
[1] Browser cache,
[2] Find the hosts file of the local machine,
[3] Routing cache,
[4] Find DNS server (local domain name, top-level domain name, root domain name) - Iterative analysis and recursive query.
IP—DNS service—an easy-to-remember domain name
The domain name consists of dots, letters and numbers, and is divided into top-level domains (com, cn, net, gov, org), second-level domains (baidu, taobao, qq, alibaba), and third-level domains Domain (www) (12-2-0852)

.2 Detailed explanation of DHCP protocol
DHCP (Dynamic Configuration Protocol: Dynamic Host Setting Protocol): It is a LAN protocol and an application layer protocol that uses UDP protocol. Function: Automatically assign IP addresses to users who temporarily access the LAN.
.3 HTTP protocol detailed explanation
File Transfer Protocol (FTP): Control connection (port 21): Transmit control information (connection, transmission request), in 7-bit ASCII code format. Stay on for the entire session.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol: Hypertext Transfer Protocol) [TCP, port 80]: It is a reliable data transmission protocol. Before the browser sends and receives messages to the server, it first establishes a TCP connection. HTTP uses the TCP connection method (HTTP itself has no connection ).
HTTP request message method:
GET: Request the specified page information and return the entity body;
POST: Submit data to the specified resource for processing the request;
DELETE: Request the server to delete the specified page;
HEAD: Request to read the header of the information identified by the URL. , only the message header is returned;
OPETION: Requests information about some options;
PUT: Stores a document under the specified URL.


.3.1 HTTP working structure

.3.2 Detailed explanation of HTTPS protocol
HTTPS (Secure) is a secure HTTP protocol, port number 443. Based on the HTTP protocol, it provides encrypted data processing, verification of the other party's identity, and data integrity protection through SSL or TLS.





![Computer Networking Course - Network Engineering [CompTIA Network+ Exam Prep] - DayDayNews](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/qiQR5rTSshw/hq720.jpg?sqp=-oaymwEcCNAFEJQDSFXyq4qpAw4IARUAAIhCGAFwAcABBg==&rs=AOn4CLBkfLxip0rt_UU-2cCPDV8MOpTYvw)












