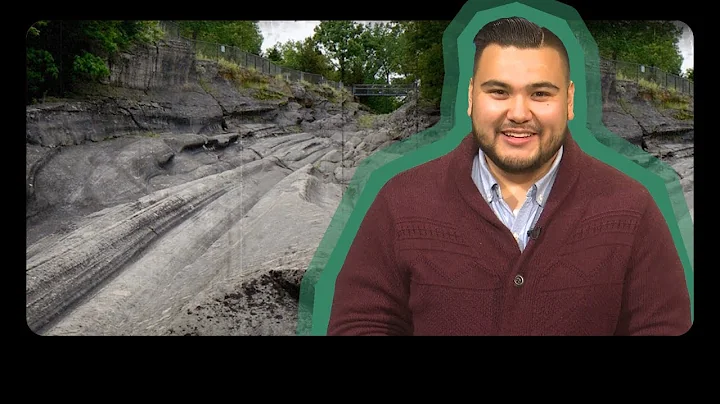
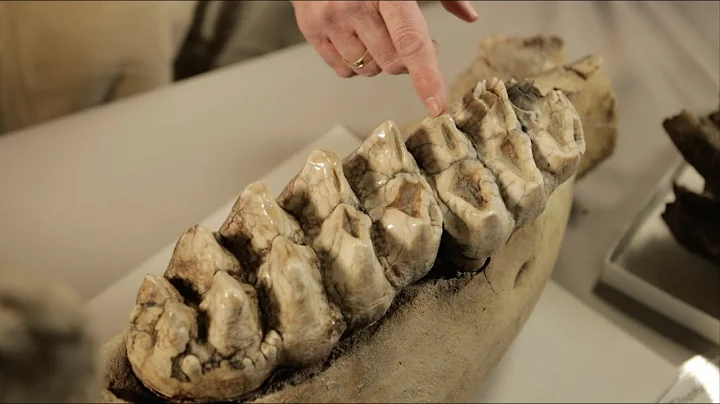
Mastodon skeleton excavated at Heath Golf Course, Ohio, December 1989. The skeleton, discovered by workers digging a pond, is more than 11,000 years old.
First of all, what is the Ice Age? When the Earth is at low temperatures for long periods of time—millions to tens of millions of years—it causes ice caps and glaciers to cover large areas of its surface.
We know that Earth has had at least five major ice ages. The first occurred about 2 billion years ago and lasted about 300 million years. The most recent one started about 2.6 million years ago, and in fact, we are still technically there.
So why isn’t the Earth covered in ice now? This is because we are in a period known as an "interglacial period." During ice ages, temperatures fluctuated between cooler and warmer levels. Ice sheets and glaciers melt during warmer phases, called interglacials, and expand during cooler phases, called glaciers.
Right now, we are in the warm interglacial period of the most recent ice age, which began about 11,000 years ago.
What was the Ice Age like? When most people talk about the "ice age," they are usually referring to the last ice age, which began about 115,000 years ago and ended about 11,000 years ago with the beginning of the current interglacial period.
During that time, the earth was much cooler than it is now. At its peak, when the ice sheet covered much of North America, the average global temperature was about 46 degrees Fahrenheit (8 degrees Celsius). That's 11 degrees Fahrenheit (6 degrees Celsius) cooler than today's global annual average temperature.
This difference may not sound like much, but it resulted in much of North America and Eurasia being covered in ice sheets. The Earth is also drier and sea levels are much lower because most of the Earth's water is trapped in ice caps. Prairies or dry grassy plains are common. The same goes for savannas or warm grassy plains and deserts.
Many of the animals that emerged during the Ice Age will be familiar to you, including brown bears,caribouand wolves. But there are also giant animals that became extinct at the end of the Ice Age, such as the mammoth, the mastodon, the saber-toothed cat, and the giant ground sloth.
There are different opinions as to why these animals became extinct. One is that when they came into contact with megafauna, humans hunted them to extinction.
Wait, there were still humans in the Ice Age? ! Yes, people like us lived through ice ages. Since our species, Homo sapiens, emerged in Africa about 300,000 years ago, we have spread throughout the world.
During the Ice Age, some populations remained in Africa and did not experience the full effects of the cold. Others moved to other parts of the world, including the cold glacial environments of Europe.
They are not alone. At the beginning of the Ice Age, there were other human species across Eurasia - including our direct ancestors and our closest relatives - such as the Neanderthals in Europe and the mysterious Denisovans in Asia. Both groups appear to have become extinct before the end of the Ice Age.
There are many ideas about how our species survived the Ice Age when our human cousins did not. Some believe it has to do with our ability to adapt and how we use social and communication skills and tools. During the Ice Age, humans didn't seem to have bowed their heads. Instead, they moved to new areas.
It has long been thought that humans did not enter North America until the ice caps began to melt. But fossil footprints found in New Mexico's White Sands National Park suggest humans were in North America at least 23,000 years ago — near the peak of the last Ice Age.