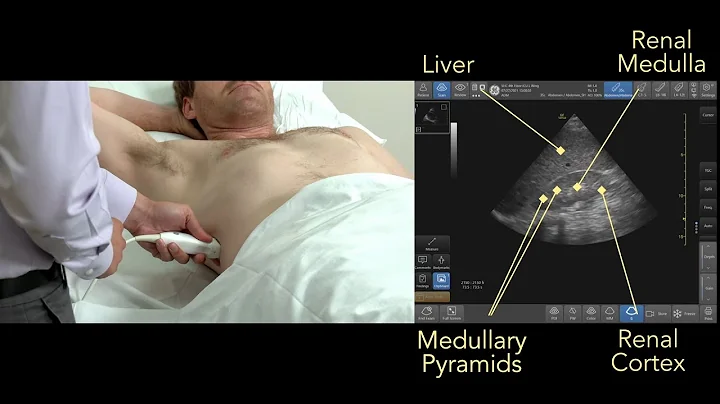
Ultrasound testing is a very important non-invasive testing method for kidney diseases, which can provide doctors with a variety of information. Ultrasound testing is divided into B ultrasonic , Doppler, contrast-enhanced ultrasound and elastography. Physicians need to choose the appropriate ultrasonic testing method according to the patient's individual conditions. However, some detection methods are relatively mature and have a high penetration rate; some examinations are developing rapidly and have a low penetration rate; and some detection methods are still in their infancy and have not yet matured. So how should doctors choose ultrasound examination methods?
In April 2022, a research team from Canada published precautions on kidney ultrasound testing in Kidney Medicine. This article introduces what you need to pay attention to in B-ultrasound, Doppler, contrast-enhanced ultrasound and elastography. In addition, the article believes that elastography may replace the need for renal biopsy in fibrotic kidneys in the future, that is, non-invasive detection of renal fibrosis.
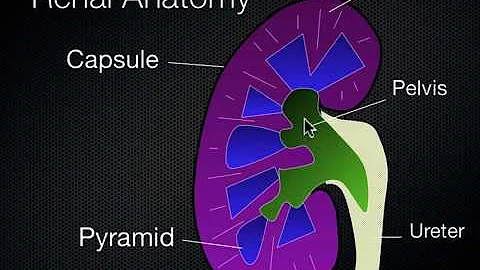
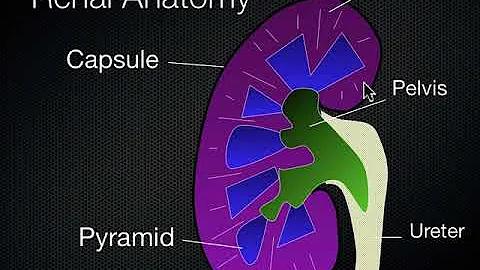
B-ultrasound
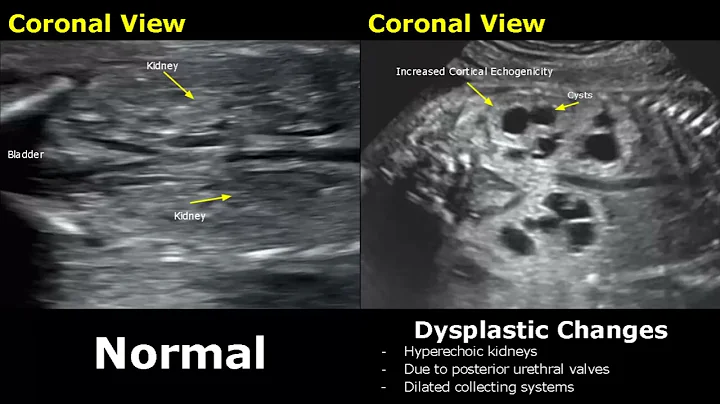
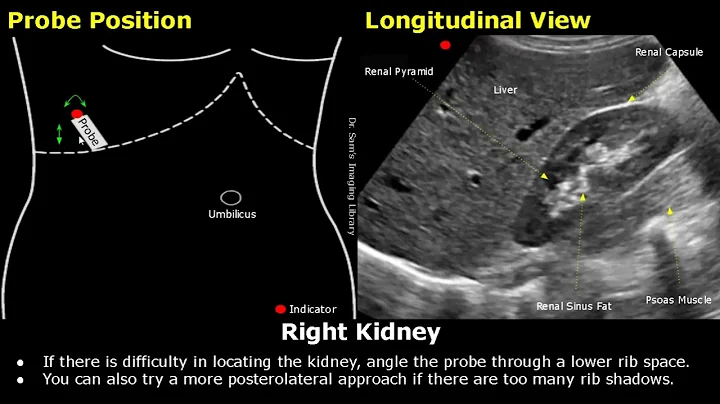
B-ultrasound is a two-dimensional, grayscale anatomical cross-sectional depiction image, which has been widely used in clinical practice. The principle of B-ultrasound is related to the difference in tissue density resulting in different reflected waves of ultrasound . These reflected waves are converted by electronic computers to form visual images that can be used for diagnosis. Currently, the role of ultrasound in kidney testing includes measuring the length and volume of the kidneys.
1 Kidney length
Kidney length is defined as the maximum distance between the two poles. Usually the left kidney is longer than the right kidney, and the normal range of both kidneys is 10~12cm. The median size of the left kidney was 11.2 cm and that of the right kidney was 10.9 cm. The normal cortical thickness of the kidney is 7~10mm.
Widjaja et al found a moderate positive correlation between estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and kidney length (R²=0.48). In addition, some scholars have found that reduced cortical thickness may be related to the progression of kidney disease or the decline of eGFR.
2 Kidney volume
Kidney volume is related to gender. The normal range for men is 110~190ml, and for women it is 90~150ml. At present, the measurement of kidney volume is usually simplified to a spherical or elliptical shape for rough calculation. However, the standard method should be to draw a kidney volume model through multiple multi-directional detections. It is worth noting that the results of ultrasound detection of kidney volume may not be accurate. Kim et al. found that compared with CT, ultrasound detection underestimated kidney volume by about 15%.
Nephrology physicians can understand the progression of kidney disease through the above parameters. Kidney length ≤8cm is closely related to renal failure. If the above situation occurs on one side, or is related to atrophy or fibrosis, it especially indicates insufficient perfusion (such as renal artery stenosis .) If the volume of the kidneys is reduced on both sides, it indicates the onset of kidney disease. In advanced stages, such as renal failure.
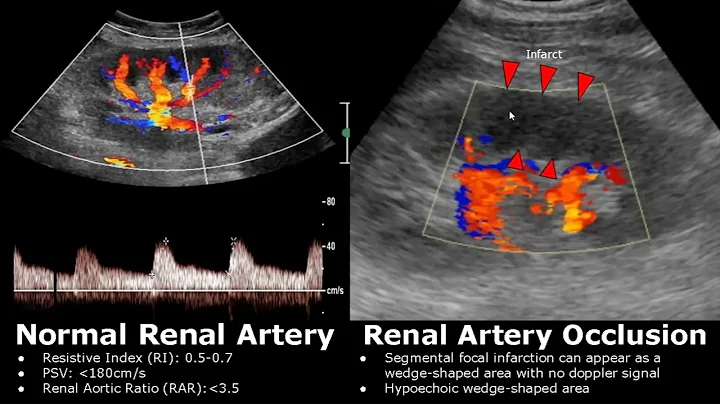
Doppler Imaging
Unlike B-ultrasound, Doppler imaging can be used to evaluate blood flow and normal conditions in the renal vessels. Doppler ultrasound is used more often to evaluate transplanted kidneys than native kidneys. However, it can be used to detect conditions of renal vascular disease such as stenosis or thrombosis . A systematic review found that Doppler ultrasound has a higher sensitivity (85%) and specificity (92%) for peak systolic velocity than other ultrasound tests. Doppler can also detect renal venous thrombosis as kidney size increases and renal parenchymal vascular flow is reversed. More importantly, Doppler has high sensitivity and can detect small vascular changes, such as capillary changes.
Doppler ultrasound can obtain the patient's renal artery resistance index (RRI). RRI ≤ 0.7 indicates that the native kidney has not been seriously damaged. However, what exactly abnormal RRI represents is controversial.
On the one hand, some studies believe that increased RRI values are related to glomerulosclerosis , glomerular disease , arteriolar sclerosis and interstitial fibrosis, but other studies have not found a correlation. Many scholars believe that elevated RRI may have a high prognostic value, that is, RRI is associated with worsening renal function and cardiovascular risk scores. Furthermore, Wang et al reported that the RRI of deceased donor kidneys (0.73±0.10) was higher than that of living donor kidneys (0.66±0.11). However, no studies have confirmed that RRI is a predictor of outcome of renal transplantation, including long-term renal allograft survival.
On the other hand, some researchers believe that the RRI does not reflect changes in the kidney itself, but rather reflects the value of extra-renal variables. RRI is affected by age, heart rate, blood pressure, systemic vascular resistance and hydration. This theory applies not only to native kidneys but also to transplanted kidneys. Many studies have shown that caution should be used when interpreting RRI and extrarenal factors in the patient need to be considered.
More importantly, the value of Doppler ultrasound is easily affected by external factors. Operator proficiency, sensor location, and Doppler model may affect accuracy and repeatability. If the medical facility does not have an experienced operator, it is best to just use Doppler ultrasound to check for patency.
contrast-enhanced ultrasound
super contrast-enhanced ultrasound is based on conventional ultrasound examination. It enhances human blood flow signals by intravenously injecting ultrasound contrast agent , and observes tissue microvascular perfusion information dynamically in real time to improve the detection rate of lesions and detect lesions. It is a non-invasive and radiation-free technology to identify benign and malignant tumors. The examination process is relatively short. Although contrast-enhanced ultrasound is less expensive than color Doppler imaging, in the clinic, contrast-enhanced ultrasound is more accurate in assessing stenotic arteries and requires less operator effort.
contrast-enhanced ultrasound can improve the visualization of perfusion and provide quantitative values such as time-intensity curves, time-peak parameters, etc. by observing the flow of contrast agent . Therefore, contrast-enhanced ultrasound can assess ischemic diseases such as infarction or necrosis or even malignant renal injury.
Ma et al studied the role of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in 33 patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and diabetes. They found that the total area of the time-intensity curve was moderately correlated with eGFR, and that there were significant differences in time-peak parameters between early-stage and late-stage CKD patients. In addition, some researchers have found that time-peak parameters are significantly different in patients with suspected CKD compared with healthy people.
Some published data suggest that contrast-enhanced ultrasound can identify abnormalities in renal function in kidney transplant recipients. Compared with controls, the time for contrast medium to reach the cortex from the renal artery was significantly increased in acute rejection patients. In a systematic review of 524 patients after renal transplantation, the sensitivity of contrast-enhanced ultrasound was 86%, the specificity was 90%, and the area under the curve was 0.94.
Currently, contrast-enhanced ultrasound is used more in tumor examinations and less in kidney examinations. Therefore, medical practitioners may conduct in-depth research in this area to determine appropriate contrast agents, equipment, and even procedures and parameters.
Elastography
Currently, the “gold standard” for kidney disease is renal biopsy. However, renal biopsy is an invasive examination and has potential complications. Some researchers believe that elastography may become an alternative to kidney biopsy, and more importantly, elastography is completely non-invasive.
Elastography is used to measure tissue elasticity, allowing "palpation" under the skin. Compared with ordinary ultrasound testing, the pulse wave speed of elastography is slower, so it can detect the deformation of organs, and when combined with other operations (such as external pressure or internal pressure), the tissue elasticity can be known. Taking renal fibrosis as an example, currently it can only be determined by the degree of collagen deposition and extracellular matrix increase in postoperative renal biopsy specimens. However, elastography can further understand the elasticity of the kidney and determine the degree of fibrosis. Some scholars have found that when the cutoff value is 0.93, elastography will help detect CKD, with a sensitivity of 88% and a specificity of 95%. Bob and other researchers found that the elasticity of the kidneys of patients with late-stage CKD was significantly lower than that of patients with early-stage CKD. However, some researchers have found that elastography cannot fully reflect the "elasticity" of the patient's kidneys.
In kidney transplant recipients, elastography can predict the progression of renal lesions, but there is controversy regarding renal cortical stiffness. Some scholars have found a significant association between median medullary sclerosis and fibrosis. Using elastography and machine learning, Urban et al. were able to differentiate between fibrosis, inflammation, and fibrosis+inflammation in kidney transplant recipients.
However, although elastography is exciting, it is still in its early stages. At present, humans have little experience with it, and there are countless attributions for some variations in elastography.For example, blood pressure and urinary pressure can cause anisotropy of the kidney; the direction of the nephron can also affect the "elasticity"; it is also controversial whether the heart and respiratory cycles affect elastography. If researchers can overcome the above problems and form a complete model, non-invasive methods for detecting renal fibrosis markers will be available.
Reference:
1. Singla RK, Kadatz M, Rohling R, et al. Kidney Ultrasound for Nephrologists: A Review. Kidney Med. 2022 Apr 7;4(6):100464.