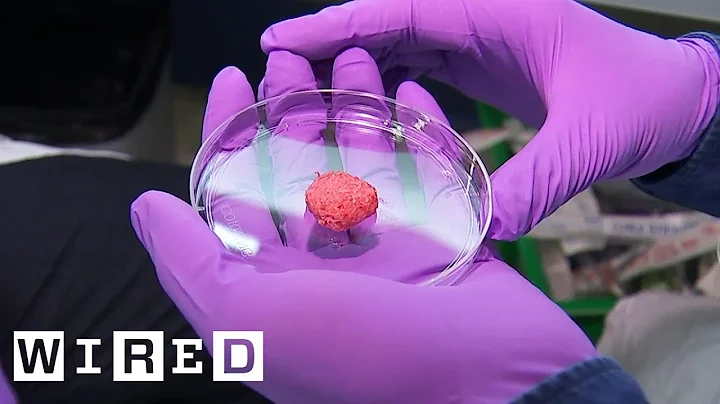
Right now we may be experiencing the beginning of the next food revolution - cellular agriculture, which is growing meat from cells.
In addition to being used in medicine and other fields, biotechnology has also been widely used in the food field in recent years, such as the production of artificial meat.
Just as cars made horse-drawn carriages a thing of the past and disappeared from people’s sight, artificial meat developed based on biotechnology may completely change the relationship between humans and animals. In the future, people may be able to eat beef and chicken without raising and slaughtering animals.
Replacing slaughtered meat with artificial meat not only has ethical significance, but also has a positive impact on the ecological environment and economic development.
As we all know, the use of fossil fuels such as oil and coal will produce a large amount of carbon dioxide , exacerbating global warming. In fact, animal breeding is also one of the sources of air, land and ocean pollution that cannot be ignored. In addition, the production of meat products also consumes a lot of resources. In the words of an artificial meat practitioner: "Eating less chicken can save more water than not taking a shower for half a year."
Some people also believe that the actual carbon footprint or pollution produced by artificial meat is likely to be no more than that of traditional farms. How much better. In this regard, Paul Shapiro, author of Clean Meat: How Growing Meat Without Animals Will Revolutionize Dinner and the World, said: " There is very strong evidence that the production of artificial meat uses far less land and water than actually raising animals.”

图|Paul Shapiro (Source: Data map)
It is understood that chickens are tightly packed in modern industrial farms. In extremely small cages, not only do animals suffer unprecedented suffering, but they are also more likely to cause deadly bird flu epidemics. Despite the help of vaccines, pesticides, etc., diseases cannot be completely avoided.
More importantly, the demand for meat around the world is still growing rapidly. Can humans keep raising and slaughtering livestock endlessly to meet all needs? Just looking at population growth alone, broadening people's meat choices would also be a good thing.
At present, compared with the plant-based meat that is already available on the market and is made of plant protein as raw material, the development of artificial meat using cell culture is more difficult, but it is also considered by the industry to be a more ideal alternative to slaughtered meat.
An early method of culturing cell-cultured meat is to use animal muscle satellite cells, whose only function is to produce muscle. They are taken out and placed in a culture medium where they will eventually grow into real meat.
It is worth mentioning that the cell meat cultured in this way has already passed the trial stage. In 2013, a tasting was held for the first cultured beef burger. The burgers at that time were still lacking in taste due to their single ingredients and lack of blood, fat, and connective tissue found in animal meat. It is also very expensive to produce, with the entire process costing about $330,000 (about 2 million yuan).
However, with the advancement of technology, the subsequent production cost of cell-based meat has gradually decreased. Just 2 years later, the cost to make the same burger dropped by 80%. Around 2021, the cost of cell-cultured chicken produced by Future Meat, an Israeli artificial meat company, has been less than 300 yuan per kilogram.
“Costs are already coming down at a rapid rate. As for taste, ultimately, these artificial products will be indistinguishable from slaughter-based meat products. They are real, real animal meat, just straight from the meat. grown in cells," Shapiro said.
In the field of artificial meat, more and more start-up companies are emerging.For example, China's Zhou Ziwei, CellX and other companies are conducting research and development of cell-cultured meat. Among them, Zhou Ziwei released China's first cell-cultured pork belly on June 10 this year and began small-scale production of the product.
Some foreign companies are also producing artificially cultivated chicken sandwiches, mayonnaise , tuna , collagen and other products.
At present, if artificial meat wants to meet commercial standards, it must further reduce costs, improve taste and find better ways of mass production. After all, people will only be willing to consume artificial meat that is delicious, cheaper, and healthier.

(Source: Data map)
As one of the first people in the world to try artificial meat, Shapiro wrote "Artificial Meat" in order to let more people understand this emerging field that may solve global problems. The book comprehensively displays the progress of artificial meat in the laboratory, the commercialization process, overcoming cost reduction and government regulatory obstacles, how to compete with industrial animal husbandry for the market, etc., and predicts future dietary trends.
The original title of this book is "Clean Meat", which literally translates as "clean meat" and is another name for cell-based meat in the West. Shapiro also has his own understanding of the name: "'Clean meat' is a recognition of clean energy and the food safety benefits of producing real meat without animals. This kind of meat is better for the earth." Cleaner and safer for humans. For example, handling raw meat can be dangerous due to the presence of enteric pathogens such as E. coli and Salmonella . "Clean meat" eliminates the need to worry about the presence of enteric pathogens.
Some artificial meat experts have predicted that "the global artificial meat market share will reach 60% by 2040."
Shapiro said that predicting the future 20 years from now is difficult, but it is possible. After all, it was hard to imagine in 1990 that you could have instant video communication with almost anyone in the world for next to nothing, and a world without slaughterhouses might soon be a reality.
-End-