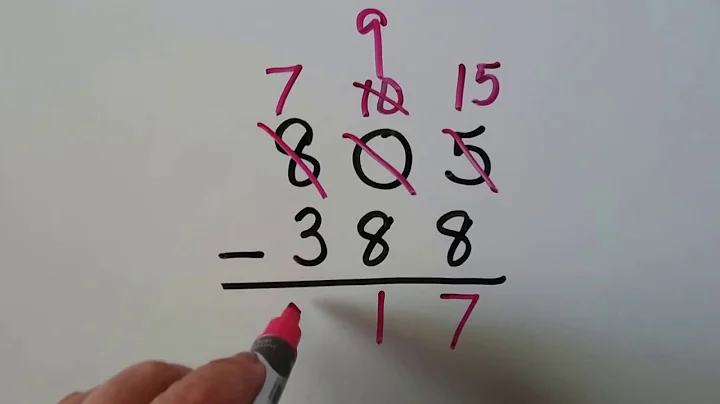Primary school mathematics rules knowledge classification
(1) Two-digit addition in writing, three things to remember:
1. Align the same digits;
2. Add from the ones digit;
3. When the ones digit reaches 10, advance 1 to the tens digit.
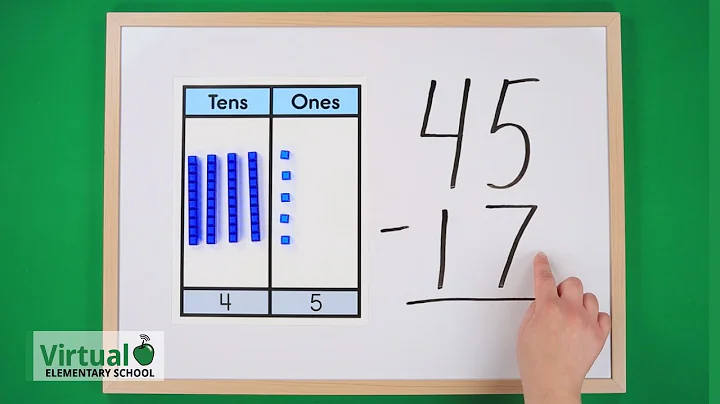
(2) When subtracting two-digit numbers in writing, you should remember three things:
1. Align the same digits;
2. Subtract from the ones digit;
3. If the ones digit is not enough to subtract, go back 1 from the tens digit, add 10 to the ones digit and then subtract.
(3) Mixed operation calculation rules
1. In the calculations without brackets, if there are only additions, subtractions or only multiplications and divisions, they must be operated in order from left to right;
2. In the calculations without brackets, there are multiplications, divisions and For addition and subtraction, you must first calculate multiplication and division and then addition and subtraction;
3, if there are parentheses in the calculation, you must calculate what is inside the parentheses first.
(4) The four-digit reading method
1, read in order from the high digit, the thousands place is read as thousands, the hundreds place is read as hundreds, and so on;
2, there is one 0 or two 0s in the middle Only read one "zero";
3, no matter how many zeros there are at the end, it will not be read.
(5) Four-digit writing method
1, starting from the highest digit, write in order;
2, if it is thousands, write the number in the thousands place, if it is hundreds, write the number in the hundreds place, and so on, which digit should be in the middle or at the end? If there is none, just write "0" in the bit.
(6) When subtracting four-digit numbers, you should also pay attention to three things:
1. Align the same digits;
2. Subtract from the ones digit;
3. If any digit is not enough to subtract, return 1 from the previous digit, add 10 to the base digit, and then subtract.
(7) Multiplication rules for multiplying one digit by multiple digits
1. Starting from the ones digit, multiply each digit in the multi-digit number by one digit in turn;
2. Whichever digit the product of which is multiplied by the highest number reaches tens? A few steps forward.
(8) The divisor is a one-digit division rule
1. Starting from the high-digit division of the dividend , each time the divisor is used, try to divide the previous digit of the dividend. If it is smaller than the divisor, try to divide the first two digits. ;
2. Whichever digit the divisor reaches, write the quotient on that digit;
3. Every time a quotient is found, the remaining number must be smaller than the divisor.
(9) A factor is the multiplication rule for two-digit numbers.
1. First use the number in the two-digit ones digit to multiply another factor, and the last digit of the number will be aligned with the two-digit ones digit;
2. Then use Multiply the number in the tens digit of the two-digit number by another factor, and align the last digit of the number with the two tens digits;
3, and then add the two multiplied numbers together.
(10) The rule of division when the divisor is a two-digit number
1. Starting from the high digit of the dividend, try dividing the first two digits of the dividend with the divisor. If it is smaller than the divisor,
2. Divide to whichever digit of the dividend it is. Write the quotient;
3. Every time a quotient is found, the remaining number must be smaller than the divisor.
(11) The rules for reading numbers in the ten thousand level are:
1, first read the ten thousand level, then read the next level;
2, the numbers in the ten thousand level should be read according to the reading method of the one level, and then add the word "ten thousand" at the end;
3. No matter how many 0s there are in the last digit of each level, it will not be read. If there is one 0 or several consecutive zeros in other digits, only one "zero" will be read.
(12) multi-digit reading rules
1. Starting from the high position, read one level at a time;
2. When reading hundreds of millions or ten thousand levels, read according to the reading method of series, and then add at the end Use the word "billion" or "ten thousand";
3, the 0 at the end of each level is not read, and other digits with a 0 or several consecutive 0s are only read as a zero.
(13) Comparison of decimal sizes
compares the size of two decimals. First look at their integer parts. The number with the larger integer part is larger. If the integer part is the same, the number with the larger tenth place is larger. Tenth place The numbers are also the same, the number on the percentile is larger, and so on.
(14) Decimal addition and subtraction calculation rules
calculates decimal addition and subtraction. First align the decimal points (that is, align the numbers on the same digits), then calculate according to the integer addition and subtraction rules, and finally align the horizontal lines in the resulting numbers. Click on the decimal point position on the line.
(15) Calculation rules for decimal multiplication . To calculate decimal multiplication in
, first calculate the product according to the multiplication rules, and then look at the total number of decimals in the factor. Count the number from the right side of the product and put the decimal point.
(16) The divisor is the rule of integer division. The
divisor is the decimal division of an integer. It is removed according to the rules of integer division. The decimal point of the quotient should be aligned with the decimal point of the dividend. If there is still remainder after division to the end of the dividend, it will be after the remainder. Add 0 and continue dividing.
(17) The rule of division operation when the divisor is a decimal.
When the divisor is a decimal, first move the decimal point of the divisor to make it an integer; move the decimal point of the divisor to the right by a few places, and the decimal point of the dividend also move by a few places to the right (not enough digits) Add 0 to the end of the dividend) and then perform the calculation according to the decimal division method when the divisor is an integer.
(18) Steps for answering application questions
1. Clarify the meaning of the question, find out the known conditions and the question asked, analyze the quantitative relationship in the question, and determine what to count first, what to count next, and what to count last;
2. Determine what each How to calculate in one step, list the calculation formula, and calculate the result;
3, conduct a test and write the answer.
(19) General steps for formulating equations to solve word problems
1. Understand the meaning of the problem, find the unknowns, and represent them with , check and write the answer.
(20) Rules for adding and subtracting fractions with the same denominator
Add and subtract fractions with the same denominator, the denominator remains unchanged, only the numerators are added and subtracted.
(21) Rules for addition and subtraction of mixed fractions with the same denominator. To add and subtract
mixed fractions, first add and subtract the integer part and the fraction part respectively, and then combine the resulting numbers.
(22) Rules for adding and subtracting fractions with different denominators
To add and subtract fractions with different denominators, first make the common denominator, and then calculate according to the rules for adding and subtracting fractions with the same denominator.
(23) Calculation rules for multiplying fractions by integers
When multiplying fractions by integers, use the product of the numerator of the fraction and the integer as the numerator, and the denominator remains unchanged.
(24) Calculation rules for multiplying fractions by fractions
When multiplying fractions by fractions, the product of multiplying the numerators is used as the numerator, and the product of multiplying the denominators is used as the denominator.
(25) Calculation rule for dividing a number by a fraction
Dividing a number by a fraction is equal to multiplying the number by the reciprocal of the divisor.
(26) How to convert decimals into percentages and percents into decimals
To convert decimals into percentages, just move the decimal point two places to the right and add a percent sign at the end;
converts percentages into decimals, put the percent sign Remove it and move the decimal point two places to the left.
(27) Methods of converting fractions into percentages and percentages into fractions.
converts fractions into percentages. Usually, the fractions are converted into decimals first (three decimal places are usually reserved for indivisible divisions), and then the decimals are converted into percentages;
converts percentages into decimals. First rewrite the percentage as a fraction whose denominator is 100, and reduce the fraction that can be reduced to the simplest fraction.

Primary school mathematics oral definition classification
1. What is the perimeter of a figure? The sum of the lengths of all sides surrounding a figure in
is the perimeter of the figure.
2. What is area? The size of the surface of
objects or the surrounding plane graphics is called their area.
3. The relationship between the parts of addition:
One addend = sum - another addend
4. The relationship between the parts of subtraction:
Minuend = minuend - difference Minuend = subtrahend + difference
5. Between the parts of multiplication The relationship between:
one factor = product ÷ another factor
6. The relationship between the parts of division:
divisor = dividend ÷ quotient dividend = quotient × divisor
7. Angle
(1) What is an angle? In
, the shape formed by two rays drawn from a point is called an angle.
(2) What is the vertex of an angle? In
, the endpoints forming an angle are called vertices.
(3) What is the side of an angle? In
, the rays surrounding the angle are called the sides of the angle.
(4) What is a right angle?
An angle with a degree of 90° is a right angle.
(5) What is a square angle? The two sides of an
corner are in a straight line, and such an angle is called a straight angle.
(6) What is an acute angle?
angles less than 90° are acute angles.
(7) What is an obtuse angle?
An angle greater than 90° and less than 180° is an obtuse angle.
(8) What is the circumference angle?
The angle formed by a ray rotating around its endpoint is called a circumferential angle. A circumferential angle is equal to 360°.
8. Perpendicular questions
(1) What is mutual perpendicularity? What is vertical line ? What is compared to ?
When two straight lines intersect at right angles, the two lines are perpendicular to each other. One of the straight lines is called the perpendicular to the other straight line. The intersection of the two straight lines is called the vertical foot.
(2) What is the distance from a point to a straight line?
draws a vertical line from a point outside the straight line to a straight line. The distance between the point and the vertical foot is called the distance from this point to the straight line.
9. Triangle
(1) What is a triangle? In
, a shape surrounded by three line segments is called a triangle.
(2) What are the sides of a triangle? Each line segment that forms a triangle in
is called a side of the triangle.
(3) What are the vertices of a triangle? In
, the intersection of every two line segments is called the vertex of the triangle.
(4) What is an acute triangle?
A triangle with three acute angles is called an acute triangle.
(5) What is a right triangle?
has a triangle with a right angle called a right triangle.
(6) What is an obtuse triangle?
has a triangle with an obtuse angle called an obtuse triangle.
(7) What is isosceles triangle ?
A triangle with two equal sides is called an isosceles triangle.
(8) What is the waist of an isosceles triangle? In
, in an isosceles triangle, the two equal sides are called the waist of the isosceles triangle.
(9) What are the vertices of an isosceles triangle? The intersection of the two waists of
is called the vertex of the isosceles triangle.
(10) What is the base of an isosceles triangle?
In an isosceles triangle, the side that is not equal to the other two sides is called the base of the isosceles triangle.
(11) What are the base angles of an isosceles triangle? The two equal angles on the base of
are called the base angles of an isosceles triangle.
(12) What is an equilateral triangle?
A triangle with three equal sides is called an equilateral triangle, also called an equilateral triangle.
(13) What is the height of a triangle? What is the base of a triangle?
draws a vertical line from a vertex of a triangle to its opposite side. The line segment between the vertex and the vertical foot is called the height of the triangle. The side opposite this vertex is called the base of the triangle.
(14) What is the sum of the interior angles of a triangle?
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°.
10. Quadrilateral
(1) What is a quadrilateral? In
, a shape surrounded by four line segments is called a quadrilateral.
(2) What is an equal quadrilateral?
A quadrilateral with two parallel sides is called parallelogram .
(3) What is the height of a parallelogram?
draws a perpendicular line from a point on one side of a parallelogram to the opposite side. The line segment between this point and the vertical foot is called the height of the quadrilateral.
(4) What is a trapezoid?
only has a set of parallel quadrilaterals called trapezoids.
(5) What is the base of a trapezoid?
A set of equal sides in a trapezoid is called the base of the trapezoid (usually the shorter base is called the upper base, and the longer base is called the lower base).
(6) What is the waist of a trapezoid?
In a trapezoid, an unequal set of opposite sides is called the waist of the trapezoid.
(7) What is the height of a trapezoid?
draws a vertical line from one point on the upper bottom to the lower bottom. The line segment between this point and the vertical foot is called the height of the trapezoid.
(8) What is an isosceles trapezoid?
A trapezoid with two equal sides is called an isosceles trapezoid.
11. What are natural numbers? The 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10... used by
to represent the number of objects are natural numbers (natural numbers are all integers).
12. What is rounding method?
When finding the approximate number of a number, look at the number in the highest digit of the omitted mantissa. If it is 4 or smaller than 4, round off the mantissa. If it is 5 or larger than 5, after removing the mantissa, Add 1 to its previous digit. This method of finding approximate numbers is called the rounding method.
13, the meaning of addition and the laws of operation
(1) What is addition? In
, the operation of combining two numbers into one number is called addition.
(2) What is an addend? The two numbers added in
are called addends.
(3) What is and? The result of adding
addends is called sum.
(4) What is the commutative law of addition?
When two numbers are added and the positions of the addends are exchanged, their sum remains unchanged. This is called the commutative law of addition.
14. What is subtraction?
It is known that the sum of two numbers and one of the addends, the operation of finding the other addend is called subtraction.
15. What is the minuend? What is a subtraction? What is difference?
In subtraction, the known sum is called the minuend, the known number subtracted is called the subtrahend, and the unknown number sought is called the difference.
16. The relationship between the various parts of addition:
Sum = addend + addend Addend = sum - another addend
17. The relationship between the various parts of subtraction:
Difference = Minuend - Minuend Minuend = Minuend -Difference minuend = subtrahend + difference
18, multiplication
(1) What is multiplication?
's simple operation of finding the sum of several identical addends is called multiplication.
(2) What is a factor? The two numbers multiplied by
are called factors.
(3) What is product? The number obtained by multiplying the
factors is called the product.
(4) What is the commutative law of multiplication?
When two factors are multiplied, the positions of the factors are exchanged, and their product remains unchanged. This is called the commutative law of multiplication.
(5) What is the associative law of multiplication? To multiply three numbers in
, first multiply the first two numbers and then multiply them by the third number, or first multiply the last two numbers and then multiply them by the first number. Their product remains unchanged. This is called the associative law of multiplication.
19. Division
(1) What is division?
knows the product of two factors and one of the factors, and the operation of finding the other factor is called division.
(2) What is the dividend? In
division, the known product is called the dividend.
(3) What is the divisor? In
division, a known factor is called the divisor.
(4) What is a business? In
division, the unknown factor found is called the quotient.
20. The relationship between the various parts of multiplication:
product = factor ) The relationship between the various parts of division with remainder:
dividend = quotient × divisor + remainder
22. What is a nominal number?
The number that is usually measured and the name of the unit is called a nominal number.
23. What is a singular number?
A number with only one unit name is called a single number.
24. What is a plural number?
A number with two or more unit names is called a complex number.
25. What is a decimal?
imitates the writing method of integers, written on the right side of the integer digits, separated by dots, and the numbers used to express tenths, hundredths, thousandths... are called decimals.
26. What are the basic properties of decimals?
Add zero or remove zero from the end of a decimal, and the size of the decimal remains unchanged. This is called the basic property of decimals.
27. What is a finite decimal?
A decimal with a finite number of digits in the decimal part is called a finite decimal.

28. What is an infinite decimal? A decimal with infinite digits in the decimal part of
is called an infinite decimal.
29. What is a loop section?
A number whose recurring decimal part appears repeatedly in sequence is called the recurring section of this number.
30. What is a pure recurring decimal?
cyclic sections starting from the first decimal place are called pure cyclic decimals.
31. What is a mixed recurring decimal?
loop sections that do not start from the first decimal part are called mixed loop decimals.
32. What are the four arithmetic operations? In
, we collectively refer to the four operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division as the four arithmetic operations.
33. What is an equation?
An equation containing unknown numbers is called an equation.
34. What is solving an equation? The process of finding solutions to equations in
is called solving equations.
35. What is a multiple? What is a divisor?
If a can be divided by b , a is a multiple of b, and b is called the divisor of a (or the factor of a).
36. What kind of number can be divisible by 2? HTML numbers with 6 digits of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 can all be divisible by 2.
37. What is an even number?
A number that is divisible by 2 is called an even number.
38. What is an odd number?
A number that is not divisible by 2 is called an odd number.
39. What kind of number can be divisible by 5?
numbers that are 0 or 5 can be divisible by 5.
40. What kind of number can be divisible by 3?
If the sum of the digits of a number is divisible by 3, then the number will be divisible by 3.
41. What is a prime number (or prime number)?
If a number has only two divisors, 1 and itself, such a number is called a prime number.
42. What is a composite number?
A number has other divisors besides 1 and itself. Such numbers are called composite numbers.
43. What is a prime factor? In
, every composite number can be written as the multiplication of several prime numbers. Each prime number is a factor of the composite number and is called a prime factor of the composite number.
44. What is decomposition of prime factors?
expresses a composite number in the form of multiplying prime factors, which is called decomposing prime factors.
45. What is the common divisor? What is the greatest common divisor? The common divisors of several numbers in
are called common divisors. The largest one is called the greatest common divisor.
46. What are coprime numbers?
Two numbers whose common divisor is only 1 are called coprime numbers.
47. What is a common multiple? What is the least common multiple? The common multiples of several numbers in
are called the common multiples of these numbers. The smallest one is called the least common multiple of these numbers.
48, fraction
(1) What is a fraction?
divides unit 1 into several equal parts, and the number of such parts or parts is called a fraction.
(2) What is the score line? In
, the horizontal line in the middle of the score is called the score line.
(3) What is the denominator? The part below the
fraction line is called the denominator.
(4) What is a molecule? The part above the
score line is called the numerator.
(5) What is a fractional unit?
divides the unit "1" evenly into several parts, indicating that one part is called a fractional unit.
49. How to compare fractions?
(1) For two fractions with the same denominator, the fraction with the larger numerator is larger.
(2) For two fractions with the same numerator, the smaller denominator has a larger numerator.
(3) What is a true score?
The fraction whose numerator is smaller than the denominator is called a proper fraction.
(4) What is an improper fraction?
A fraction in which the numerator is greater than the denominator or the numerator and denominator are equal is called an improper fraction.
(5) What is a mixed number?
numbers composed of integer fractions and proper fractions are usually called mixed numbers.
(6) What are the basic properties of fractions? The numerator and denominator of a
fraction are multiplied or divided by the same number (except 0) at the same time, and the size of the fraction remains unchanged. This is the basic property of fractions.
(7) What is reduction?
converts a fraction into a number that is equal to it but has a smaller numerator and denominator, which is called a reduction.
(8) What is the simplest fraction?
The fraction whose numerator and denominator are coprime is called the simplest fraction.
50, ratio
(1) What is ratio?
The division of two numbers is also called the ratio of two numbers.
(2) What is the first term of comparison? The number in front of the
ratio sign is called the preceding term of the ratio.
(3) What is the consequent of comparison? The number after the
ratio sign is called the consequent term of the ratio.
(4) What is ratio? The quotient obtained by dividing the former term of the
ratio by the latter term is called the ratio.
(5) What are the basic properties of ratio? The former and posterior terms of the
ratio are multiplied or divided by the same number at the same time (except 0) and the ratio remains unchanged. This is called the basic property of the ratio.
51, cuboid and cube
(1) What is an edge? The edge where two faces intersect in
is called an edge.
(2) What is vertex? In
, the point where three edges intersect is called a vertex.
(3) What are the length, width and height of a cuboid?
The lengths of the three edges that intersect at a vertex are called the length, width, and height of the cuboid respectively.
(4) What is a cube (cube)?
A rectangle with equal length, width and height is called a cube (or cube).
(5) What is the surface area of a cuboid? The total area of the six faces of the
cuboid is called the surface area of the cuboid.
(6) What is object volume? The size of the space occupied by an
object is called the volume of the object.
52, circle
(1) What is the center of a circle? The point in the center of the
circle is called the center of the circle.
(2) What is radius?
The line segment connecting the center of the circle and any point on the circle is called the radius.
(3) What is diameter?
The line segment that passes through the center of the circle and has both ends on the circle is called the diameter.
(4) What is the circumference of a circle?
The curve that forms a circle is called the circumference of the circle.
(5) What is pi?
We call the ratio of the circumference and diameter of a circle pi.
(6) What is the area of a circle? The size of the plane enclosed by the
circle is called the area of the circle.
(7) What is a fan shape?
The figure enclosed by an arc and two radii passing through both ends of the arc is called a fan shape.
(8) What is arc? In
, the part between two points on a circle is called an arc.
(9) What is the central angle? The angle between the
vertex at the center of the circle is called the central angle.
(10) What is a symmetrical graphic?
If a graphic is folded in half along a straight line and the graphics on both sides can completely overlap, such a graphic is a symmetrical graphic.
53. What is a percentage?
means that the number that represents one percent of another number is called a percentage, and a percentage is also called a percentage or a percentage.
54, proportion
(1) What is proportion?
means that two equations with equal ratios are called proportions.
(2) What is a proportional item? The four numbers that make up the ratio in
are called the items of the ratio.
(3) What are proportional exceptions? The two items at both ends of
are called proportional extra terms.
(4) What is the proportional inner term? The two middle items in
are called proportional inner terms.
(5) What is the basic property of proportion? In
, the product of two external terms in a ratio is equal to the product of two internal terms.
(6) What is solution ratio? The unknown term in finding the proportion in
is called solving the proportion.
(7) What is the proportional relationship? There are two related quantities in
. When one quantity changes, the other quantity also changes. If the ratio (that is, the quotient) of the two corresponding numbers in the two quantities is constant, the two quantities are called proportional quantities. Their The relationship is called a direct proportional relationship.
(8) What is the inverse proportional relationship? There are two related quantities in
. If one changes, the other will also change. If the corresponding product of the two quantities is constant, the two quantities are called inversely proportional quantities, and their relationship is inversely proportional.
55, cylinder
(1) What is the base of a cylinder? The upper and lower surfaces of the
cylinder are called the bottom surface of the cylinder.
(2) What are the sides of a cylinder? The curved surface of the
cylinder is called the side surface of the cylinder.
(3) What is the height of a cylinder? The distance between the two bases of an
cylinder is called the height of the cylinder.

The calculation unit and progress rate classification
1, the length measurement unit and progress rate:
kilometers (kilometers), meters, decimeters, centimeters, millimeters
1 kilometers = 1 kilometer 1 kilometer = 1000 meters
1 meters = 10 Decimeter 1 decimeter = 10 centimeters
1 centimeters = 10 millimeters
2, area measurement unit and rate:
square kilometers, hectares, square meters, square decimeters, square centimeters
1 square kilometers = 100 hectares
1 square kilometers = 1,000,000 square meters
1 hectares = 10,000 square meters
1 square meters = 100 square decimeters
1 square decimeters = 100 square centimeters
3, volume measurement units and rates:
cubic meters, cubic decimeters, cubic centimeters, liters, milliliters
1 Cubic meter = 1000 cubic decimeter
1 cubic decimeter = 1000 cubic centimeter
1 cubic decimeter = 1 liter 1 cubic centimeter = 1 milliliter
4, mass unit and rate:
tons, kilograms, kilograms, grams
1 tons = 1000 kilograms
1 Kilogram = 1 kilogram
1 kilogram = 1000 grams
5, time unit and progress rate:
century, year, month, day, hour, minute, second
1 century = 100 years 1 year = December
1 days = 24 hours 1 hour = 60 Minutes
1 minutes = 60 seconds
(31-day months include 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, and December, 30-day months include 4, 6, 9, and November, February in ordinary years has 28 days, and 2 in leap years Month 29 days)
Common calculation formula table
1, rectangular area
= length × width, calculation formula S=ab
2, square area
= side length × side length, calculation formula S=a×a=a2
3, rectangle perimeter
=(length + width)×2, calculation formula C=(a+b)×2
4, perimeter of square
=side length×4, calculation formula C=4a
5, area of parallelogram
=base × height, calculation Formula S=ah
6, triangle area
=base×height÷2, calculation formula S=a×h÷2
7, trapezoid area
=(upper base+lower base)×height÷2, calculation formula S=(a+ b)×h÷2
8, the volume of the cuboid
= length × width × height, the calculation formula V = abh
9, the area of the circle
= pi × radius square, the calculation formula V = πr2
10, the volume of the cube
= edge length × edge Length END ——
Note: The content comes from the Internet, and the copyright belongs to the original author and original source. If there is any infringement, please contact us.
- For more primary school learning materials, please pay attention to "16 student guide to learn " and send a private message to "primary school materials" to get for free.
follow @16 student guide and never miss the educational information you need!